Unit 9: Ecology and the environment.
Ecology
Click here to do an ecology lab!
ENVIROMENTAL FACTORS The environmental factors are all the components of an ecosystem, whose presence or variation influences the organism that from the biocenosis. The environmental factors can be abiotic and biotic. Abiotic. These factors are the physical and chemical elements of an ecosystem. The most important abiotic factors are: - Temperature; most living things cannot live at temperature below 0ºC or above 50ºC). - Light; essential for autotrophic organisms. - Water; without water life cannot exist. Biotic. These factors refer to any organism or the behavior of any organism which affects the life of the other organisms within the system. We can distinguish intraspecific and interspecific relationships:Ecology is the study of organisms and their interactions with the environment. Ecologists study living things at a range of scales.
An ecosystem is a system formed of the biocenosis and biotope; the relationships established between the populations of living things form the biocenosis, while the relationships with the physical factors constitute the biotope. A population is a group of individuals of the same species that have the ability to reproduce amongst themselves.
Species
As a reproductive unit.
The species is the taxonomic unit that describes all organisms capable of reproducing by producing fertile offspring.
As a unit of evolution.
Due to reproduction, each species is also the unit of evolution. Given that each species is the result of interbreeding between members over the length of their history, member organisms are more closely related to each other than to any other organisms. So they have in common certain structural and functional characteristics and share the species’ gene pool.
As an ecological unit.
Being evolutionary units, all species are also ecological units. Each one is defined by its ecological niche: its place in nature (it lives in a certain environment, it uses certain materials, it eats certain types of food, with certain habits, it reproduces following certain habits, etc.)
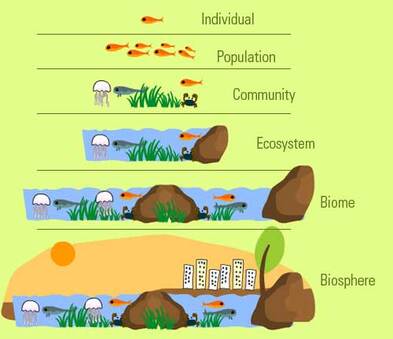
Population:
A population is a group of individuals of the same species that have the ability to reproduce amongst themselves
Community:
This includes all the populations in a specific area at a given time
Ecosystem:
Ecosystems include a community of living organisms (biotic) interacting with the environment (abiotic).
Biome:
A set of ecosystems sharing similar characteristics
Biosphere:
A biosphere is the sum of all the ecosystems established on planet Earth.
Environmental factors
The environmental factors are all the components of an ecosystem, whose presence or variation influences the organism that from the biocenosis. The environmental factors can be abiotic and biotic.
Abiotic
These factors are the physical and chemical elements of an ecosystem. The most important abiotic factors are: - Temperature; most living things cannot live at temperature below 0ºC or above 50ºC). - Light; essential for autotrophic organisms. - Water; without water life cannot exist.
Biotic
These factors refer to any organism or the behavior of any organism which affects the life of the other organisms within the system. We can distinguish intraspecific and interspecific relationships:
Intraspecific relationships are relationships between members of the same species. The most important are competition, where animals compete for resources such as food, mates, territory, etc., and associations, including related individuals (family) or not related (gregarious).
Interspecific relationships are relationships between members of different species. They are classified according to the effects that individuals of interacting species have on each other, using symbols:
– (negative effects)
+ (positive effect)
0 (no effects).
Some of the most common are Competition (-,-); Predation (+,-); Parasitism (+,-); Commensalism (+,0) and Mutualism (+,+).

