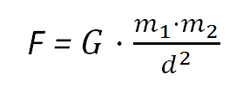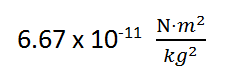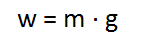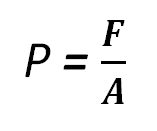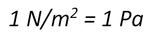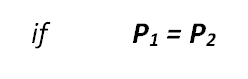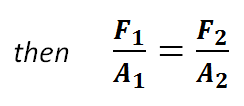Unit 7 - Forces
|
Key concept - Change- Past of an object in motion can be reconstructed and future foreseen on the basis of the current state and the forces acting upon it
Related concepts - Patterns and Motion- Motion and forces can be expressed in mathematical equations Global concept - Scientific and Technical Innovation- Constant parallel improvement of science and technology can provide answers to some of human questions about the universe.. |
Key words
|
|
|
7a. Newton´s 3 principles of motionPrinciples of motion
1st - Unless acted on by a force, an object with remain at rest or at a constant velocity.
2nd - Force = mass x acceleration 3rd - When one body exerts a force on a second body, the second body exerts a force of equal magnitude and opposite direction on the first. |
You will be required to use F = m·a along with the equations seen in unit 6. The only extra information required to calculate the force would be the mass of the object.
| |||
Task 7a. Complete the following problems:
- A 1500 kg car starts from a standstill and accelerates to a velocity of 20 m/s in 10 s. It then hits a concrete wall. What is the force produced by this impact?
- Calculate the force exerted by a 100 g apple dropped from a height of 10 m. (This is a trick question)
- What will be the final velocity of a 500 kg motorbike that starts at a standstill, drives for 8 s and then produces a force of 500 N when it hits the back of a truck. (Luckily nobody is hurt!)
|
7a ANSWERS
|
| ||
7b. The law of universal gravitation
This relates the force of gravity (F), the universal gravitational constant (G), the masses of the 2 objects (m1 and m2 in kg) and the distance between them (d).
This law shows that the gravitational attraction between 2 bodies is:
- Directly proportional to the mass of the objects
- Inversely proportional to the distance squared
|
Task 7b: Consider the following theory questions using the equation above: (Hint: imagine the masses and distance both begin as 1 unit)
1. Dawn wants to make as much money as possible by selling gold. Her plan involves buying gold by the weight at one altitude and then selling it at another altitude at the same price per weight. Should Dawn buy at a high altitude and sell at a low altitude or vice versa? 2. Suppose that two objects attract each other with a gravitational force of 16 units. If the distance between the two objects is doubled, what is the new force of attraction between the two objects? |
3. Suppose that two objects attract each other with a gravitational force of 16 units. If the distance between the two objects is reduced in half, then what is the new force of attraction between the two objects?
4. Suppose that two objects attract each other with a gravitational force of 16 units. If the mass of both objects was doubled, and if the distance between the objects is also doubled, then what would be the new force of attraction between the two objects? |
|
Extension:
When comparing mass and size data for the planets Earth and Jupiter, it is observed that Jupiter is about 300 times more massive than Earth. One might quickly conclude that an object on the surface of Jupiter would weigh 300 times more than on the surface of the Earth. For instance, one might expect a person who weighs 500 N on Earth would weigh 150000 N on thesurface of Jupiter. Yet this is not the case. In fact, a 500-N person on Earth weighs about 1500 N on the surface of Jupiter. Explain how this can be. |
ANSWERS: 1. Buy at high altitudes and sell at low altitudes. 2. 4 units. 3. 64 units. 4. 16 units.
7c. Types of forces
7c.i. Gravitational force
To calculate the force due to gravity here on Earth (weight or w) we can substitute G, d (radius of the Earth) and M (mass of the Earth) to give us:
As the units for g are in N/kg, this shows that the acceleration should be the same regardless of the mass (because for every kg of mass, there is a force of 1 N). This can be seen in the videos below.
|
|
|
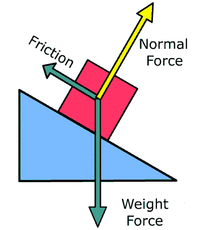
7c.ii Normal force (Fnorm)An object resting upon a surface is receiving a supporting force with a perpendicular angle to the inclination of the plane.
7c.iii. Friction (Ffrict)This is the force exerted by a surface as an object tries to move across it. It is dependent on the nature of the 2 surfaces and can be calculated with the following equation:
|
Ffrict = µ · Fnorm
Where µ is the friction coefficient between the 2 materials.
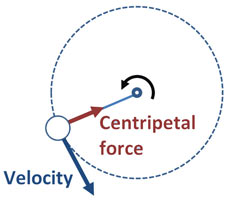
7c.iv. CentripetalThe velocity vector of an object moving in a circle is always in the direction of the tangent. This means that in circular motion, the velocity vector is constantly changing direction. Therefore a force must be acting on it towards the centre of the circle.
We call this centripetal force. |
Task 7c.i: Which of the forces above could be found on the following (focus on the most significant of the forces above):
a. Mr Polko standing in the polideportivo.
b. An atom of iron in the direct centre of the Earth.
c. The International Space Station.
d. Mr Canning going down a slide.
a. Mr Polko standing in the polideportivo.
b. An atom of iron in the direct centre of the Earth.
c. The International Space Station.
d. Mr Canning going down a slide.
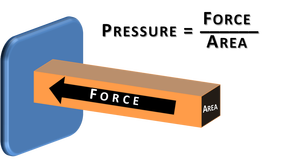
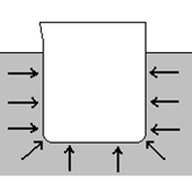
7d. PressureApplying a force to an object can cause deformation. The amount of deformation depend on both the magnitude of the force and the surface area upon which it is applied.
|
Task 7di:
ai. What is the pressure produced by a force of 15000 N acting on an area of 5 m2. ai. Explain the following demonstration in words. LINK b. Which produces a greater pressure:
|
c. A cylindrical tank with a compressible lid has a cross-sectional area of 40 cm2. What pressure is produced when a mass of 10 kg is placed on top.
ANSWERS: a. 3000 Pa; b. 2000 Pa, 1500 Pa, 800 Pa, 20000 Pa; c. 24500 Pa
7e. The fundamental hydrostatic principle
|
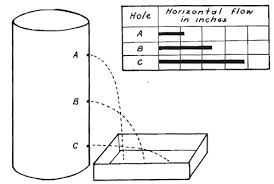
In a vertical body of water, the internal pressure is due to the downwards force caused by the mass of water above it. So at a greater depth, there is more water above, therefore a greater downwards force and a high pressure. This is why a bottle of water with 3 holes in it will project water at 3 different distances (right).
|
This is described by the fundamental hydrostatic principle. The interior pressure of a liquid of density d and depth h is:
p = h d g
|
Task 7f.i:
Extension: Why do fish eyes and stomach sometimes bulge out when they are pulled to the surface? VIDEO
|
|
This means that in an enclosed system, pressure is exerted equally and in all directions by a liquid.
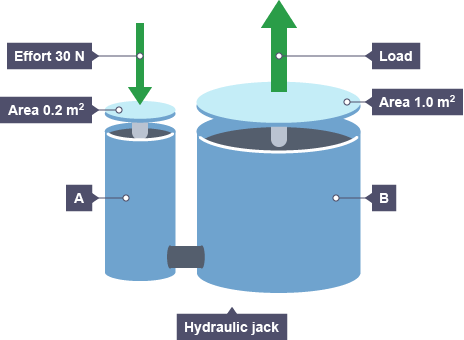
This property if liquids can be used to explain its use in hydraulic (liquid) systems. A force used on small surface area at one end of the system can be transferred to make a large force on a large surface area.
|
|
Therefore, in a liquid:
Task 7ei:
a. Show how the 30 N force on the left piston creates a 150 N force on the right one? b. What force on the left would be required to produced a force of 225 N on the right? c. If an elephant with a mass of 2 tonnes stood on the right-hand side, what mass (kg) would be the minimum required on the left-hand side, to lift the elephant? |
ANSWERS:
i. F1/A1; 30/0.2 = F2/1.0; F2 = 150 N
ii. 45 N
iii. >400 kg
i. F1/A1; 30/0.2 = F2/1.0; F2 = 150 N
ii. 45 N
iii. >400 kg
7g. Atmospheric physicsAtmospheric pressure - The pressure exerted by the atmosphere upon a body in it.
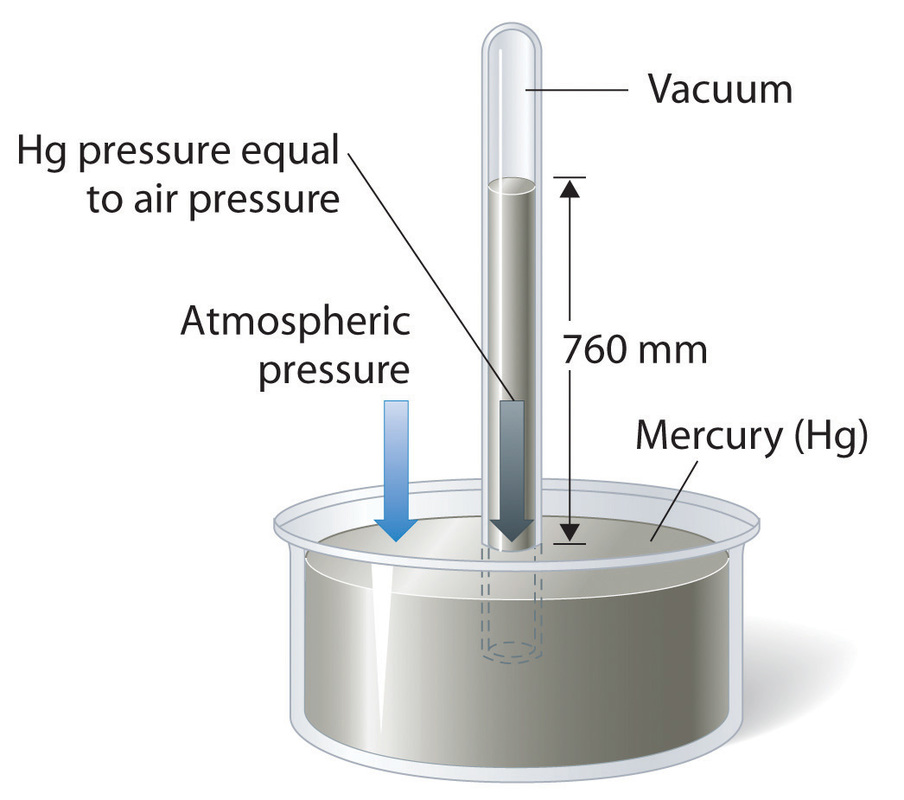
The first measurements of atmospheric pressure by Evangelista Torricelli were in units of mm Hg because of the experiment carried out. In it, a 1 m (1000 mm) was filled with mercury an inverted into a glass trough. The system reached equilibrium when the height of Hg dropped to 760 mm Hg as the pressure of the vertical Hg became equal to the pressure of the atmospheric pressure.
|
|
|
This experiment can be used to calculate atmospheric pressure in Pa and atm. 760 mm Hg = 101300 Pa = 1 atm |
Task 7gi:
a. Why might is this method of measuring pressure rarely used nowadays?
b. Suggest what would be different if this experiment was carried out at the top of Mt Everest.
a. Why might is this method of measuring pressure rarely used nowadays?
b. Suggest what would be different if this experiment was carried out at the top of Mt Everest.
7h. Archimedes principle
|
Archimedes discovered the idea that the ability of an object to float or sink in water id dependent on the amount of water displaced by that object.
|
The upward force of the water is called thrust (remember in a liquid the pressure acts in all directions) and can be calculated using the equation:
|
Fthrust = Vobject · dliquid · g
|
where d = density
and V = volume |
If the force upwards is greater than the force downwards then the object will float.
|
A complex demonstration (left) shows immiscible liquids of different densities in layers. When different objects are dropped down the column, they stop sinking when then mass of the liquid displaced is more than that of the object.
Task 7h:
a. An object of unknown mass is place in a swimming pool full of milk. If the density of the milk is 1040 kg/m3 and the thrust created by the milk is 5096 N, what is the volume of the object? And in cm3? b. A child gets into a pool, dislodging water with a weight of 300 N. What is the thrust receiving? What is the mass of the boy? c. Why might the same boat sink further when travelling in a river compare to when it is travelling at sea? |
7i - Hooke´s Law
|
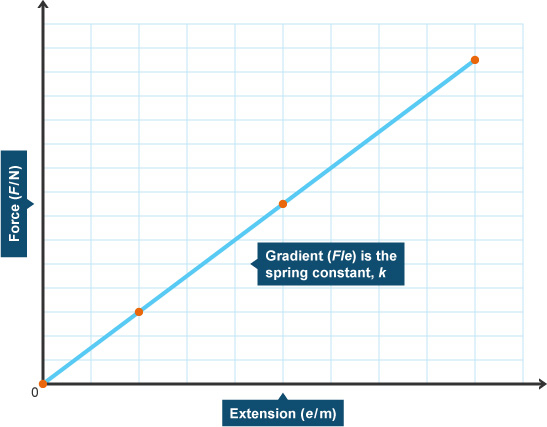
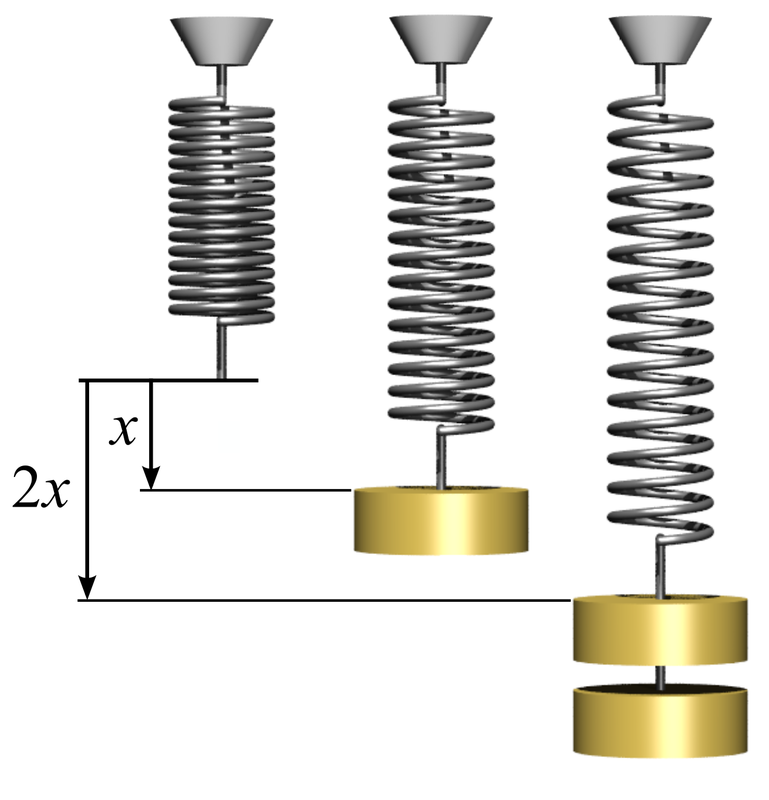
"When an elastic material is stretched, the extension (x) is directly proportional to the force (F) applied."
F = k·x
In this formula, k is the extension constant and will depend on the material. This means that a graph of F against x should look like:
|
As straight lines have the general formula: y = mx ( where m is the gradient), The gradient from the graph will be the value of k.
|
Revision
1. Mixed forces quiz
2. Unit 7 revision questions - LINK
3. Mixed theory and problem-based questions - LINK
4. Unit 7 practice test
|
| ||||