How to become a formulation hero!
Formulation is extremely important in Year 10.
This document contains all the oxidation numbers and ionic charges that you need to know:
This document contains all the oxidation numbers and ionic charges that you need to know:
| table_of_ions_yr_10_.pdf | |
| File Size: | 23 kb |
| File Type: | |
|
Official SFP guide
|
| ||||||
|
2. Now see if you can complete the following tables and practice questions:
|
| ||||||
|
3. Now try this practice test:
|
| ||||||
|
4. Mark your practice test with these answers:
|
| ||||||
|
5. 60 questions and answers:
|
| ||||||||||||
|
6. 240 questions and answers:
|
| ||||||||||||
| |||||||
Acid formulation help
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
How many acids can you find on the shelves?
Organic Formulation
Naming Organic CompoundsThe IUPAC Systematic Approach to NomenclatureA rational nomenclature system should do at least two things.:
In general, an IUPAC name will have three essential features:
• A root or base indicating a major chain or ring of carbon atoms found in the molecular structure.
• A suffix or other element(s) designating functional groups that may be present in the compound.
• Names of substituent groups, other than hydrogen, that complete the molecular structure.
As an introduction to the IUPAC nomenclature system, we shall first consider that compounds are composed only of carbon and hydrogen atoms bonded together.
- It should indicate how the carbon atoms of a given compound are bonded together.
- It should identify and locate any functional groups present in the compound. Since hydrogen is such a common component of organic compounds, its amount and locations need not be specified in most cases.
In general, an IUPAC name will have three essential features:
• A root or base indicating a major chain or ring of carbon atoms found in the molecular structure.
• A suffix or other element(s) designating functional groups that may be present in the compound.
• Names of substituent groups, other than hydrogen, that complete the molecular structure.
As an introduction to the IUPAC nomenclature system, we shall first consider that compounds are composed only of carbon and hydrogen atoms bonded together.
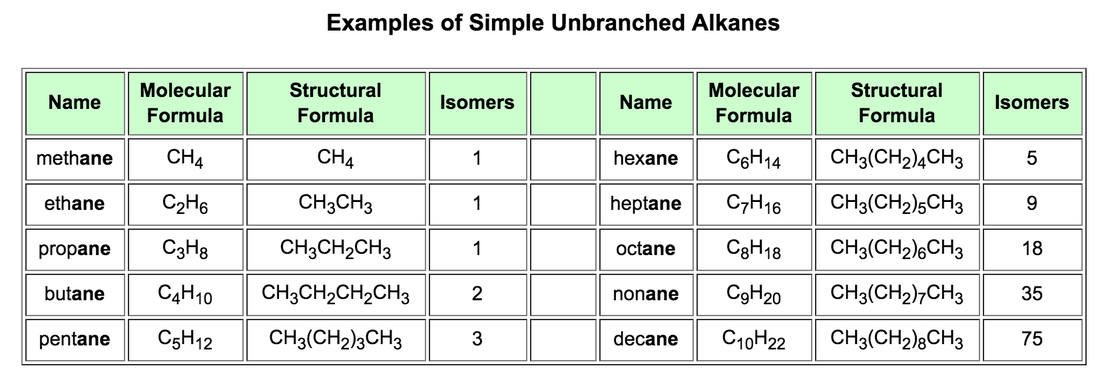
Alkanes and cycloalkanes.
Alkanes are also called paraffins due to their low reactivity (from Latin parum affinis, slight affinity).
This family comprises a very long list of compounds related to the first term of this list methane, CH4. The empirical formula of the rest can be deduced from the more general, CnH2n+2, just substituting n, by the natural entire numbers:
We call homologous series to a group of compounds that has similar structures and that are only different in the length of the carbon chain.
Alkanes are also called paraffins due to their low reactivity (from Latin parum affinis, slight affinity).
This family comprises a very long list of compounds related to the first term of this list methane, CH4. The empirical formula of the rest can be deduced from the more general, CnH2n+2, just substituting n, by the natural entire numbers:
- ethane, C2H6;
- propane, C3H8;
- butane, C4H10;
- pentane, C5H12;
- hexane, C6H14;
- heptane, octane, nonane, decane, undecane, dodecane, tridecane, etc.
We call homologous series to a group of compounds that has similar structures and that are only different in the length of the carbon chain.
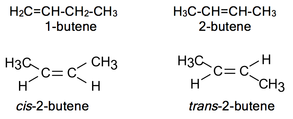
Alkenes.
Alkenes are also named olefins due to its capacity of giving oil-like halogenated derivatives. These are characterised by the presence of double bonds linking contiguous carbons. The general formula for simple alkenes (with just one unsaturation) is CnH2n. Additionally to chain isomery we can find position and geometrical isomery:
Alkenes are also named olefins due to its capacity of giving oil-like halogenated derivatives. These are characterised by the presence of double bonds linking contiguous carbons. The general formula for simple alkenes (with just one unsaturation) is CnH2n. Additionally to chain isomery we can find position and geometrical isomery:
Alkynes.
Their general formula is CnH2n-2 and they are also called acetylenic hydrocarbons alter the first term of the homologous series, el ethyne or acetylene. The functional group is a triple bond linking two carbon atoms, giving a linear molecule.
Their general formula is CnH2n-2 and they are also called acetylenic hydrocarbons alter the first term of the homologous series, el ethyne or acetylene. The functional group is a triple bond linking two carbon atoms, giving a linear molecule.
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
Some helping link for organic chemistry formulation
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Organic formulation exercises
_______________________________________________________________________________________
Organic formulation exercises
| organic_formulation_exercises.pdf | |
| File Size: | 238 kb |
| File Type: | |