The menstrual cycle
Some animations
hormones of the menstrual cycle
Video animation on the main events
The Menstrual Cycle
Women usually produced one ovum per month during her reproductive life, from puberty to middle age (menopause). The two ovaries take it in turns to produce an ovum, and one ovary releases a mature female gamete every 28 - 35 days. The cycle of producing and releasing mature ova is called the menstrual cycle. During the cycle a series of hormones will:
Women usually produced one ovum per month during her reproductive life, from puberty to middle age (menopause). The two ovaries take it in turns to produce an ovum, and one ovary releases a mature female gamete every 28 - 35 days. The cycle of producing and releasing mature ova is called the menstrual cycle. During the cycle a series of hormones will:
- prepare the uterus to receive any fertilised ova
- control the development of mature ova
Hormones affect the wall of the uterus
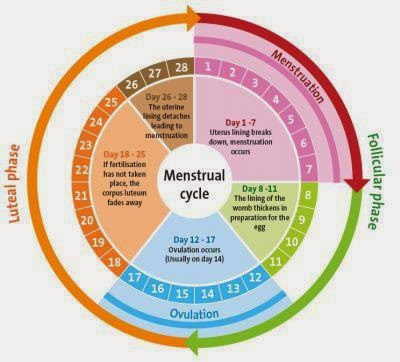
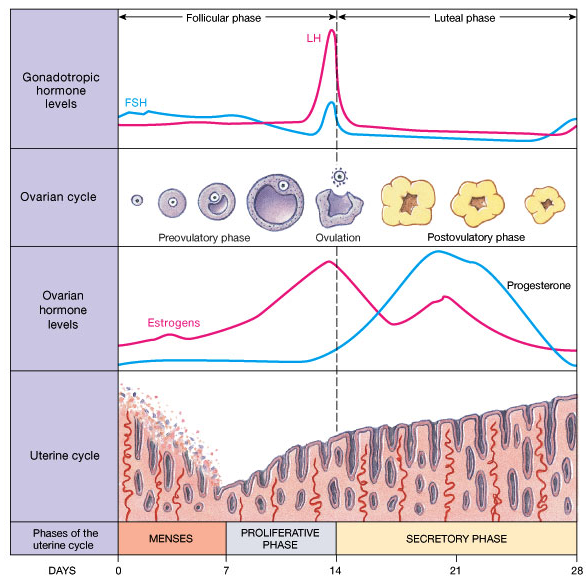
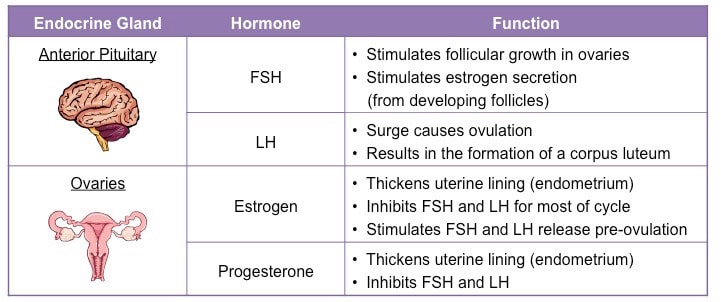
During the menstrual cycle, the wall of the uterus goes through four phases under the influence of four hormones, oestrogen, progesterone, follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and luteinising hormone (LH). During the first phase, which lasts about five days, the lining of the uterus is shed, accompanied by a loss of blood. This time is a woman’s period or more correctly the menstrual phase or menstruation. The other phases of the cycle prepare the uterus to receive and protect a zygote:
Menstruation: The uterus lining is shed. Blood and fragments of tissue leave the body through the vagina. Menstruation is triggered by a decrease in the concentration of progesterone, which is a hormone produced by the ovaries whose main role is to maintain the endometrium throughout pregnancy. On the other hand, FSH is a hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates the growth of eggs in the ovaries. The menstruation phase last from 3-7 days.
During the menstrual cycle, the wall of the uterus goes through four phases under the influence of four hormones, oestrogen, progesterone, follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and luteinising hormone (LH). During the first phase, which lasts about five days, the lining of the uterus is shed, accompanied by a loss of blood. This time is a woman’s period or more correctly the menstrual phase or menstruation. The other phases of the cycle prepare the uterus to receive and protect a zygote:
Menstruation: The uterus lining is shed. Blood and fragments of tissue leave the body through the vagina. Menstruation is triggered by a decrease in the concentration of progesterone, which is a hormone produced by the ovaries whose main role is to maintain the endometrium throughout pregnancy. On the other hand, FSH is a hormone released by the pituitary gland that stimulates the growth of eggs in the ovaries. The menstruation phase last from 3-7 days.
Repair phase: More blood vessels grow in the lining of the uterus, and the lining thickens and becomes more stable. These changes are triggered by an increase in the concentration of oestrogen, produced by the ovaries. The repair phase lasts about 10-11 days.
Ovulation (release of the egg) occurs at the peak of oestrogen concentration and is triggered by a hormone from the pituitary gland called the luteinising hormone (LH). During this phase body temperature increases about 0.5 ºC. Some women are actually aware of the moment of ovulation.
Ovulation (release of the egg) occurs at the peak of oestrogen concentration and is triggered by a hormone from the pituitary gland called the luteinising hormone (LH). During this phase body temperature increases about 0.5 ºC. Some women are actually aware of the moment of ovulation.
|
Receptive phase: The lining of the uterus and its blood vessels are now well developed. If fertilisation has occurred the embryo can become implanted. This optimum set of conditions for implantation remains from 6-7 days after ovulation, and is maintained by an increasing concentration of progesterone. This also prevents FSH secretion which prevents the release of any more mature ova.
Premenstrual phase: The uterus lining degenerates as the progesterone concentration starts to fall unless embryo implantation has occurred, in which case progesterone keeps the lining intact to begin pregnancy. This is the last few days before menstruation. |
Make sure to understand this graph fully. Know the moment at which which hormone is active and the function of it. (So for FSH, LH, Estrogens ad Progesterone)
References
Anon, (2015). [online] Available at: http://4.bp.blogspot.com/- [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Anon, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://U1eDEukP0fA/VJkkldS8tjI/AAAAAAAAAV8/4swpyYXpoV8/s1600/menstrual%2Bcycl e%2Bchart%2B-%2B3.jpeg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Artificialinsemination.files.wordpress.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
https://artificialinsemination.files.wordpress.com/2011/04/ovary-schematic.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Cabrera Calero, A. & Sanz Esteban, M. (2011). Biología y geología, 3º ESO, Andalucía. San Fernando de Henares, Madrid: Oxford Educación.
Cycles, F. (2015). Follow the Female Ovarian and Menstrual Cycles - For Dummies. [online] Dummies.com. Available at: http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/followthefemaleovarian-and-menstrual-cycles.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Dynamisch.nu, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://dynamisch.nu/feno/afbembryoengels/83ovary.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Healthline.com, (2015). Bulbourethral Gland (Cowper's Gland) Anatomy, Function & Diagram | Body Maps. [online] Available at: http://www.healthline.com/humanbodymaps/bulbourethralcowpers-gland [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Ibbio.pbworks.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://ibbio.pbworks.com/f/1317538698/oocyte.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Img.gawkerassets.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://img.gawkerassets.com/img/19d5bsdvffcvtpng/ku-xlarge.png [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Meritnation.com, (2016). Meritnation: The No.1 Education Site with Study Material & Live Classes for CBSE, ICSE, CPT, IITJEE, AIPMT & more. [online] Available at: http://www.meritnation.com/ [Accessed 5 Feb. 2016].
Nlm.nih.gov, (2015). Sexually Transmitted Diseases: MedlinePlus. [online] Available at:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/sexuallytransmitteddiseases.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Passmyexams.co.uk, (2015). Components of Blood, Cardiovascular System - Pass My Exams:
Easy exam revision notes for GSCE Biology. [online] Available at:
http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/biology/cardiovascular-system.html#1 [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Passmyexams.co.uk, (2015). The Menstrual Cycle - Pass My Exams: Easy exam revision notes for GSCE Biology. [online] Available at:
http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/biology/menstrual-cycle-and-hormones.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Pearltrees.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://www.pearltrees.com/s/pic/or/veinsarteriescapillaries-56549509 [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Pickering, W. (2006). Complete biology for IGCSE. Oxford [England]: Oxford University Press.
Tpsbiology11student2.wikispaces.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://tpsbiology11student2.wikispaces.com/file/view/bloodcomponents.jpg/186793981/bloo dcomponents.jpg [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Urgo.co.uk, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://www.urgo.co.uk/uploadedfiles/img/images/venous-system-big-01.jpg [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Webmd.com, (2015). The Vagina (Human Anatomy): Picture, Parts, Function, Definition, and Problems. [online] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/women/picture-of-the-vagina [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Women-info.com, (2016). [online] Available at: http://www.women-info.com/ [Accessed 5 Feb.
2016].
Anon, (2015). [online] Available at: http://4.bp.blogspot.com/- [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Anon, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://U1eDEukP0fA/VJkkldS8tjI/AAAAAAAAAV8/4swpyYXpoV8/s1600/menstrual%2Bcycl e%2Bchart%2B-%2B3.jpeg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Artificialinsemination.files.wordpress.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
https://artificialinsemination.files.wordpress.com/2011/04/ovary-schematic.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Cabrera Calero, A. & Sanz Esteban, M. (2011). Biología y geología, 3º ESO, Andalucía. San Fernando de Henares, Madrid: Oxford Educación.
Cycles, F. (2015). Follow the Female Ovarian and Menstrual Cycles - For Dummies. [online] Dummies.com. Available at: http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/followthefemaleovarian-and-menstrual-cycles.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Dynamisch.nu, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://dynamisch.nu/feno/afbembryoengels/83ovary.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Healthline.com, (2015). Bulbourethral Gland (Cowper's Gland) Anatomy, Function & Diagram | Body Maps. [online] Available at: http://www.healthline.com/humanbodymaps/bulbourethralcowpers-gland [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Ibbio.pbworks.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://ibbio.pbworks.com/f/1317538698/oocyte.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Img.gawkerassets.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://img.gawkerassets.com/img/19d5bsdvffcvtpng/ku-xlarge.png [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Meritnation.com, (2016). Meritnation: The No.1 Education Site with Study Material & Live Classes for CBSE, ICSE, CPT, IITJEE, AIPMT & more. [online] Available at: http://www.meritnation.com/ [Accessed 5 Feb. 2016].
Nlm.nih.gov, (2015). Sexually Transmitted Diseases: MedlinePlus. [online] Available at:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/sexuallytransmitteddiseases.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Passmyexams.co.uk, (2015). Components of Blood, Cardiovascular System - Pass My Exams:
Easy exam revision notes for GSCE Biology. [online] Available at:
http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/biology/cardiovascular-system.html#1 [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Passmyexams.co.uk, (2015). The Menstrual Cycle - Pass My Exams: Easy exam revision notes for GSCE Biology. [online] Available at:
http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/biology/menstrual-cycle-and-hormones.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Pearltrees.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://www.pearltrees.com/s/pic/or/veinsarteriescapillaries-56549509 [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Pickering, W. (2006). Complete biology for IGCSE. Oxford [England]: Oxford University Press.
Tpsbiology11student2.wikispaces.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://tpsbiology11student2.wikispaces.com/file/view/bloodcomponents.jpg/186793981/bloo dcomponents.jpg [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Urgo.co.uk, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://www.urgo.co.uk/uploadedfiles/img/images/venous-system-big-01.jpg [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Webmd.com, (2015). The Vagina (Human Anatomy): Picture, Parts, Function, Definition, and Problems. [online] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/women/picture-of-the-vagina [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Women-info.com, (2016). [online] Available at: http://www.women-info.com/ [Accessed 5 Feb.
2016].