Topic 4 and 14 - Chemical bonding and structure
Presentations
|
4.1 Ionic bonding
|
4.2 Covalent bonding
| ||||
|
4.3 Covalent structures
| |||
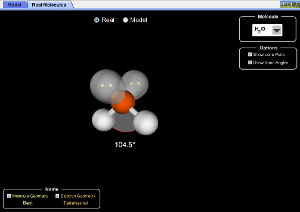
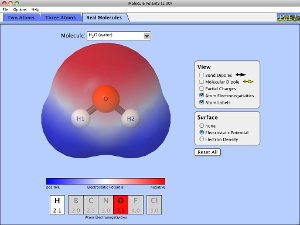
These programs are useful to help visualise the different shapes. (WARNING: The bond angles do not take into account the extra repulsion of lone pairs on the "model" page)
4.4 Intermolecular forces
| 4.4_-_intermolecular_forces.pdf |
Use this database LINK to carry out the following task.
London dispersion forces
a. Find boiling point (BP) data on the following hydrocarbon compounds - butane, octane, duodecane, hexadecane and icosane. Calculate the average BP for each and calculate the standard deviation in the values given.
b. Plot a graph of "number of carbons" against "average BP". Add error bars showing the SD.
c. Explain the trend shown.
a. Find boiling point (BP) data on the following hydrocarbon compounds - butane, octane, duodecane, hexadecane and icosane. Calculate the average BP for each and calculate the standard deviation in the values given.
b. Plot a graph of "number of carbons" against "average BP". Add error bars showing the SD.
c. Explain the trend shown.
Permanent dipole-dipole forces
a. Do the same as above with the melting points of chloromethane, chloroethane, 1-chloropropane, 1-chlorobutane and 1-chloropentane,
a. Do the same as above with the melting points of chloromethane, chloroethane, 1-chloropropane, 1-chlorobutane and 1-chloropentane,
H-bonding
a. Do as above with H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te. (You might need to use a predicted value for some of these)
a. Do as above with H2O, H2S, H2Se, H2Te. (You might need to use a predicted value for some of these)
Database task:
|
4.5 Metallic bonding
|
14.1 Covalent structures
| ||||
14.2 Hybridisation
| 14.2_-_hybridisation.pdf |
Questions
Topic 4 - Chemical bonding and structure
|
| ||||
Topic 14 - Chemical bonding and structure
|
| ||||