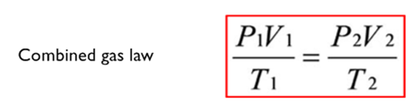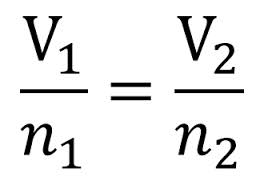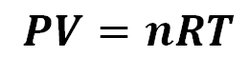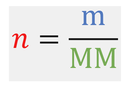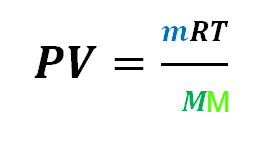Unit 2- Kinetic Theory
Ideal Gases
Key concept - Relationships - How do observable properties relate to the structure of material?
Related concepts - Models and testing - How do models of scientific phenomena evolve and what importance does experimental testing have in this process?
Global concept - Scientific innovation and technology - How has science progressed in its ability to describe the physical world?
Related concepts - Models and testing - How do models of scientific phenomena evolve and what importance does experimental testing have in this process?
Global concept - Scientific innovation and technology - How has science progressed in its ability to describe the physical world?
|
Keywords
|
|
|
Unit 2 - ANSWERS
Pre-knowledge
Heat and temperature
HEAT: Heat is the total amount of energy possesed in a substance.
TEMPERATURE: The temperature of a substance in kelvins indicates the average amount of kinetic energy possesed by its particles.
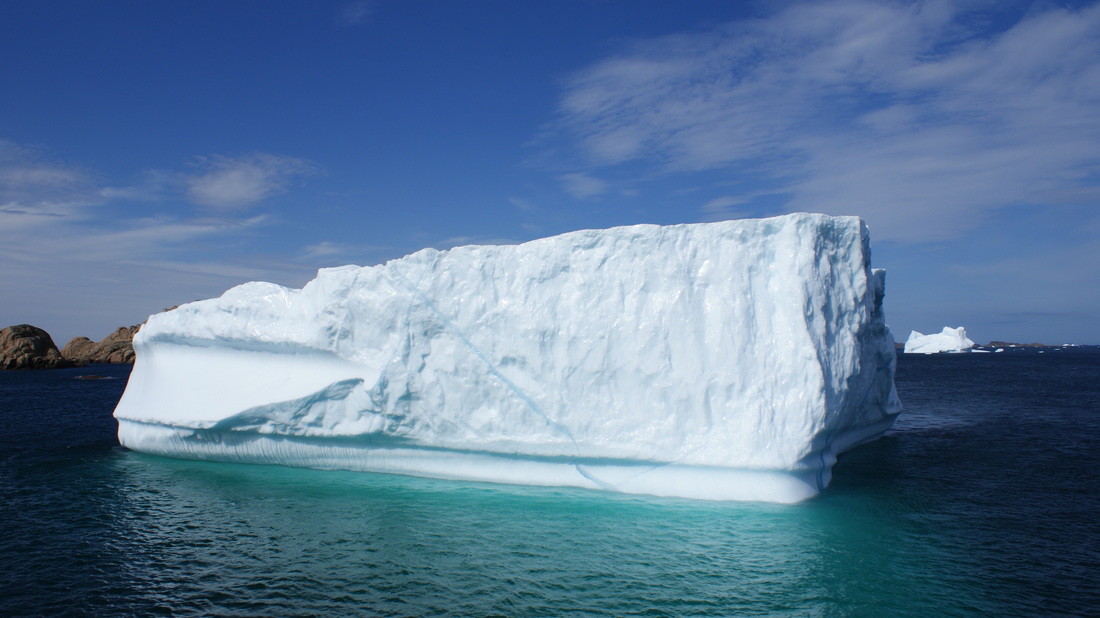
Which of the these has: a. More heat? b. A higher temperature in K? c. Stronger IMFs?
a: In this case, although each water molecule in the iceberg has little energy, there are many more molecules so the total energy will be higher.
b: In this question, the boiling water must have the highest temperature in kelvins as the average amount of kinetic energy is clearly enough to vaporise the water.
c: As both substances are made of water, the strength of the IMFs will be exactly the same.
b: In this question, the boiling water must have the highest temperature in kelvins as the average amount of kinetic energy is clearly enough to vaporise the water.
c: As both substances are made of water, the strength of the IMFs will be exactly the same.
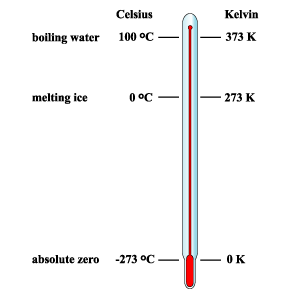
The Kelvin scale
|
The Kelvin scale is also known as the "absolute" temperature scale. This is because it starts at the lowest possible temperature that we can achieve --> 0 K.
At 0 K matter has no energy and so particles would stop moving completely. 0 K is the equivalent of -273 ºC.
|
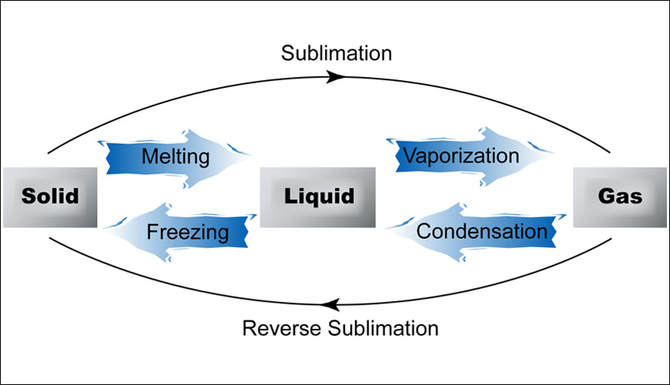
Remember and revise the states of matter and the interconversion between them.
("Interconversion Between The States of Matter - JustScience", 2018)
2.1 Kinetic theory and Ideal Gases
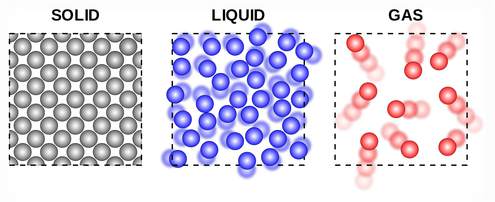
What is kinetic theory? - Kinetic theory is used to describe how particles behave in the different states of matter (solid, liquid and gas) and why they transfer between these states. We must consider the kinetic energy posessed by particles in comparison to the IMFs that hold them together.
In the solid state particles have a low energy so the intermolecular forces are strong enough to hold them tightly together in fixed positions (vibrating). Increasing the kinetic energy of particles in a solid will allow them to partially overcome intermolecular forces (IMFs) and move more freely (but still touching each other) as a liquid. As the particles gain more energy (through heating) they will eventually completely overcome the IMFs and become a gas (moving freely and in random directions).
This topic focuses mostly on kinetic theory when applied to gases:
When dealing mathematically with gases, we must make certain assumptions so that we can treat all gases with the same equations. In reality, these assumptions work well in most conditions.
The assumptions are:
When dealing mathematically with gases, we must make certain assumptions so that we can treat all gases with the same equations. In reality, these assumptions work well in most conditions.
The assumptions are:
- Particles have no intermolecular forces
- Particles have no volume
- All collisions are elastic (no energy is lost)
Task 2a:
b. High pressure (low volume) or low pressure (high volume)?
- Find a diagram of the 3 states of matter and add a description of each in your own words. (How they are arranged and how they are moving)
- What is the name of the 4th state of matter?
- Find a diagram and simple description of this state of matter.
- Explain in which conditions are the assumptions we make about ideal gases less accurate:
b. High pressure (low volume) or low pressure (high volume)?
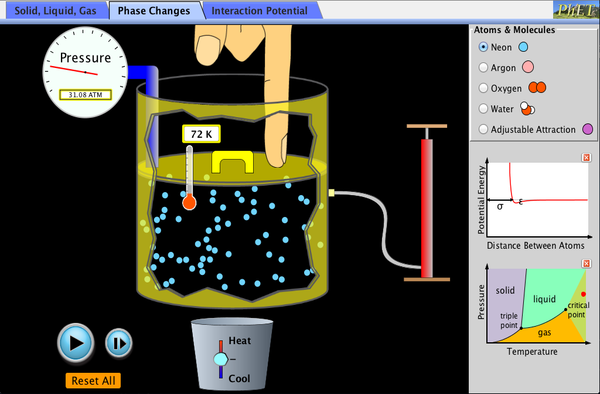
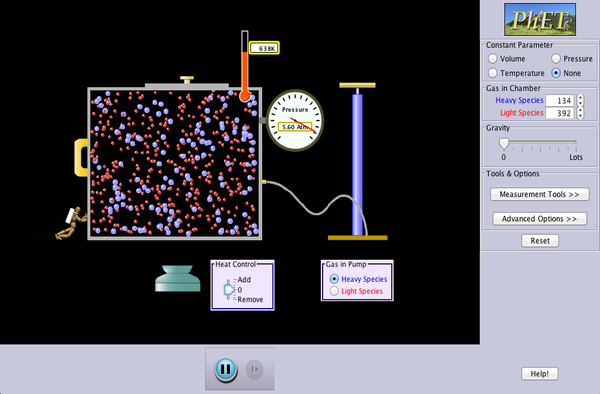
Task 2b - Don Cesar's Gas Law activity
| kinetic_theory_of_matter_simulation_investigation.docx |
|
Task 2c iii -
|
Each of the tasks can be further investigated using this simulation which allows you to select constant variables:
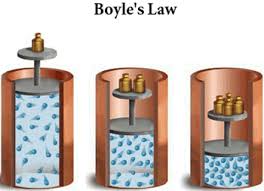
2.2 Ideal Gas Laws - P, V and T
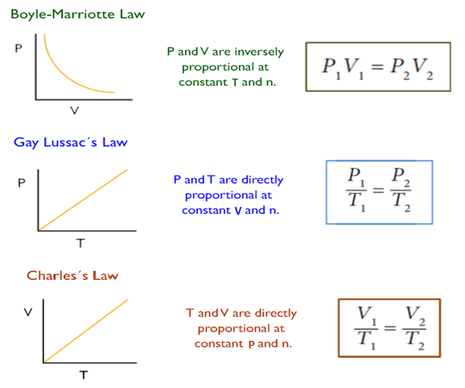
To summarise the mini-investigations into P, V, T and n, there are 3 equations we must learn that represent each of the relationships we saw. Each of these relationships is between 2 variables whilst keeping the other variables constant.
To explain each relationship we must consider:
To explain each relationship we must consider:
- The number of collisions between particles and the container.
- The force of the collisions.
The 3 equations above can be combined to give the combined gas law. There is no graph or statement as we now have 3 variables. DERIVATION
In the equations above, the units for pressure and volume do not matter (as long as you are consistent) but temperature must always be converted to Kelvin by adding 273.
e.g. 27 degrees centigrade = 300 Kelvin
e.g. 27 degrees centigrade = 300 Kelvin
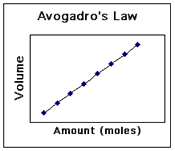
2.3 Avagadro´s Law - n
|
Italian scientist Amadeo Avagadro stated in 1811:
"At the same temperature and pressure, an equal number of moles of ANY GAS will occupy the same volume." This makes sense when we consider the assumption about ideal gases that they have no volume and no IMFs. It seems logical therefore that they will occupy the same volume. |
Avagadro also discovered to "mole" and its value of 6.02 x 10^23.
|
Task 2d:
|
Extension: How does the behaviour of real gases compare to that of ideal gases? Use diagrams and words to explain your answer.
LINK 1 LINK 2 LINK 3
LINK 1 LINK 2 LINK 3
2.4 Ideal Gas Equation
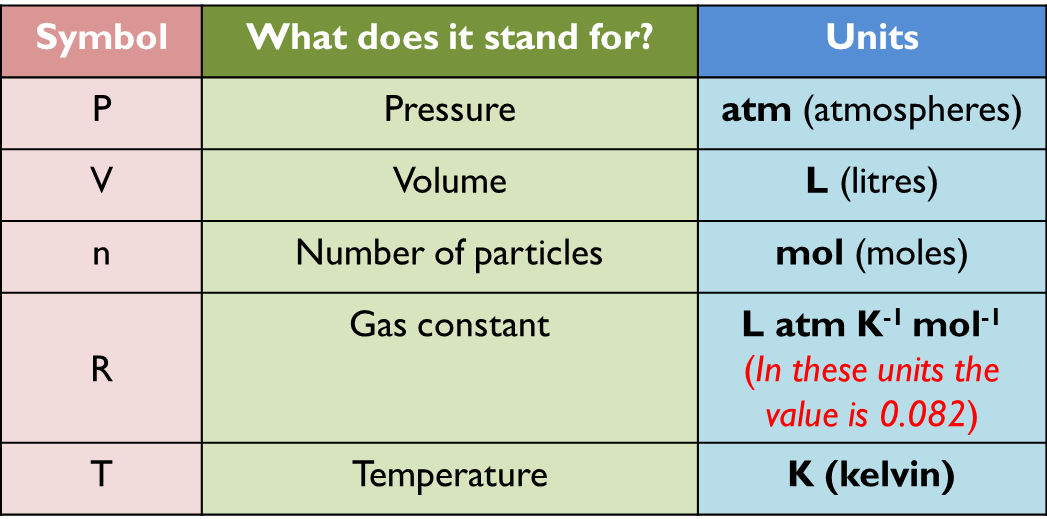
We can relate the number of moles to pressure, volume and temperature by introducing the gas constant, R. The value of this constant is 0.082 as long as we use specific units in the rest of the equation:
We may find problems that involve the calculation of a mass (g) or a molar mass (g/mol). As we know the relationship between the number of moles, mass and the molar mass is:
We can substitute this equation for n into the ideal gas equation to give one single equation: containing m and MM
Example problems using the Ideal Gas Equation: LINK
IMPORTANT NOTE: This video uses different units and a different gas constant to the ones we use in Spain!
2.5 Units and the gas laws
|
Boyle Mariotte, Gay-Lussac, Charles, Avagadro and Combined -->
|
T = kelvins
P and V = ANY units (m3, ml, atm, torr, Pa...) |
|
Ideal Gas Equation -->
|
P = atm
V = l T = kelvins n = mol |
Extension: These questions have been taken from Selectividad chemistry exams. The answers are below each one. See if you can work them out and show why!
a. 0.858 g O2 b. 0.6 litres c. 3,23 x 10^22
a. The container with ozone (O3) b. The container with ozone c. The ozone
a. Both equal b, O2 c. CH4
Revision
Gas Law Questions
|
| ||||
Gas Law Madness questions
|
| ||||
Practice exam questions
| practice_test_3-answers.docx |
| practice_test_questions.docx |
Unit 2 and 3 practice exam
|
| ||||
References