The structure of Matter
In this unit we wil continue to build on your knowledge of Matter from the previous section. You know that matter is "anything that has mass and occupies space" (Chemicool.com, 2015), and you know how to measure it and what units to use. The building blocks of matter are known as "atoms", from the Greek word meaning "un-cuttable" (Skorucak, 2015).
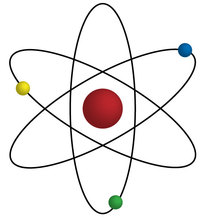
You have probably seen a picture like this before, which is one way to draw, model, an atom:
You have probably seen a picture like this before, which is one way to draw, model, an atom:
(Headberg, 2015)
But, how do we know what something looks like, if it is far too small to see?
But, how do we know what something looks like, if it is far too small to see?
Models of the Atom
People have been thinking about what their world was made of for a long time. The first recorded discussions that matter is made of particles were over 2000 years ago when a Greek named Democretus suggested that matter is made of atoms, different materials contained different types of atoms and atoms could be "re-arranged" to make different substances. However, Aristotle did not agree with Democretus so people rejected the idea until Robert Boyle came along in 1661 (Splung.com, 2015).
Boyle gave us the modern definition of an element: "An element is a substance that can not be broken down into simpler substances but can form compounds with other elements" (Splung.com, 2015). Work through the following slides for an overview of how we have our current model of the atom:
Boyle gave us the modern definition of an element: "An element is a substance that can not be broken down into simpler substances but can form compounds with other elements" (Splung.com, 2015). Work through the following slides for an overview of how we have our current model of the atom:
History of atomic theory
Task 4a: Use this website to make a timeline that summarises the discoveries that give us the model of the atom we have today.
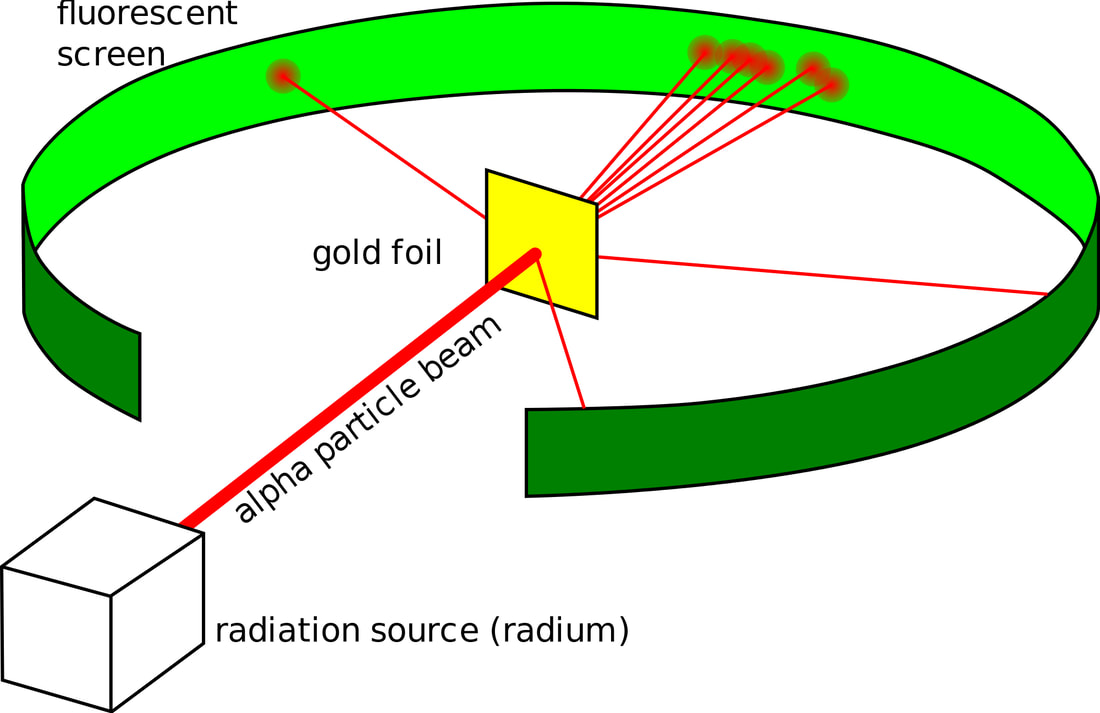
Rutherford´s experiment
Questions about Atomic Models
Task 4b: Answer the following questions in your NSD using full, clear sentences.
1. Can you name the four scientists credited with the atomic models?
2. Can you describe the differences between the original atomic model and the plum pudding model?
3. Can you find another instance where an apparent error or an accident has led to a new material or theory?
4. Can you explain why the nuclear model of the atom was not accepted until the electron shells model was presented?
5. What might have happened if Geiger and Marsden had used magnesium foil instead of gold?
6. Extension: How would you feel if you were J. J. Thomson and your atomic model was replaced in favour of the model of a student of one of your students?
Hint for question 5: Think about the sizes of the nuclei involved
1. Can you name the four scientists credited with the atomic models?
2. Can you describe the differences between the original atomic model and the plum pudding model?
3. Can you find another instance where an apparent error or an accident has led to a new material or theory?
4. Can you explain why the nuclear model of the atom was not accepted until the electron shells model was presented?
5. What might have happened if Geiger and Marsden had used magnesium foil instead of gold?
6. Extension: How would you feel if you were J. J. Thomson and your atomic model was replaced in favour of the model of a student of one of your students?
Hint for question 5: Think about the sizes of the nuclei involved
So what is the size of an atom???
References
Chemicool.com,. (2015). Definition of matter - Chemistry Dictionary. Retrieved 6 July 2015, from http://www.chemicool.com/definition/matter.html
Hedberg, J. (2015). Image of model of a classical atom by James Hedberg. Jameshedberg.com. Retrieved 6 July 2015, from http://www.jameshedberg.com/scienceGraphics.php?sort=all&id=classical_Atom_Orbits
Higheredbcs.wiley.com,. (2015). Retrieved 6 July 2015, from http://higheredbcs.wiley.com/legacy/college/olmsted/0471478113/dialogue/dialogues/info_dalton.swf
Mhhe.com,. (2015). Retrieved 6 July 2015, from http://www.mhhe.com/physsci/chemistry/essentialchemistry/flash/ruther14.swf
Skorucak, A. (2015). How did the Atom obtain it's name?. Physlink.com. Retrieved 6 July 2015, from http://www.physlink.com/Education/AskExperts/ae622.cfm
Splung.com,. (2015). The Structure of Matter. Retrieved 6 July 2015, from http://www.splung.com/content/sid/5/page/matter