The human reproductive system
INTRODUCTION VIDEO
All living organisms reproduce. Reproduction is the process by which organisms generate new individuals of the same kind ensuring continuation of the species.
There are two types of reproduction: asexual and sexual. Humans have sexual reproduction.
In sexual reproduction, genetic information from two parents combines t produce a new individual. Sexual reproduction produces individuals that are different from each other.
The process involves a number of stages. The parents have sex organs which produce sex cells or gametes. The male gamete is sperm and the female gamete is the egg.
Sexual reproduction is the fusion or fertilisation of the two male and female gametes to produce a fertilised egg or zygote. The fertilised egg goes on to divide many times to form a ball of cells. This grows into an embryo which eventually develops into a separate individual.
In humans, the organs involved in the production of the sex cells are called the gonads, the testicles in males, and the ovaries in females. Gonads also produce sex hormones.
There are two types of reproduction: asexual and sexual. Humans have sexual reproduction.
In sexual reproduction, genetic information from two parents combines t produce a new individual. Sexual reproduction produces individuals that are different from each other.
The process involves a number of stages. The parents have sex organs which produce sex cells or gametes. The male gamete is sperm and the female gamete is the egg.
Sexual reproduction is the fusion or fertilisation of the two male and female gametes to produce a fertilised egg or zygote. The fertilised egg goes on to divide many times to form a ball of cells. This grows into an embryo which eventually develops into a separate individual.
In humans, the organs involved in the production of the sex cells are called the gonads, the testicles in males, and the ovaries in females. Gonads also produce sex hormones.
| female_reproductive_system.docx |
| male_reproductive_system.docx |
Male reproductive system
The male reproductive system has two functions:
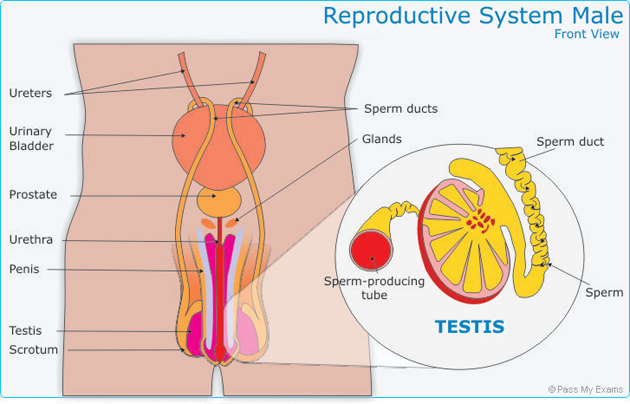
Testicles (or testes)
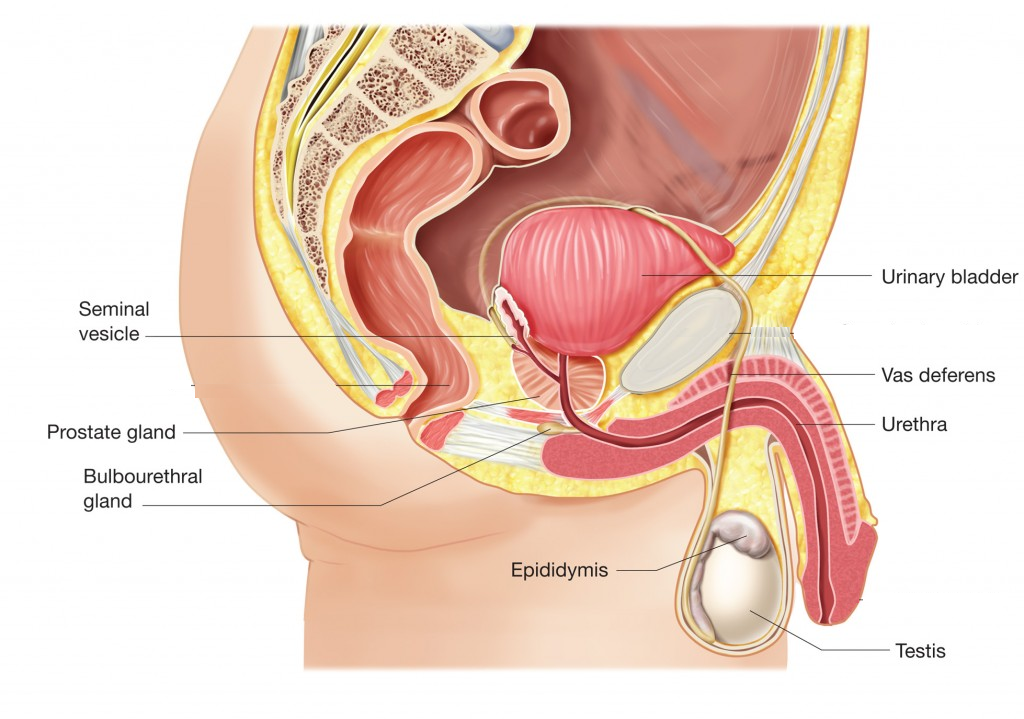
Male gonads are called testicles. These two organs are composed of numerous coiled tubes (seminiferous tubules) where we find the cells that produce the spermatocytes (precursors of sperm cells). Additionally, it is in the testicles where the male hormone, testosterone, is produced and released in the bloodstream.
The testes are enclosed in a sac of skin called the scrotum, which hangs outside the body between the legs. This keeps them at a temperature 2-3 ºC lower than body temperature, best for development of the sperm.
The sperm is transported and stored in a series of tubes until it is released from the tip of the penis. These tubes are known as the reproductive ducts:
There are as well a number of glands that secrete substances that mix with the sperm to produce a fluid called semen.
Penis
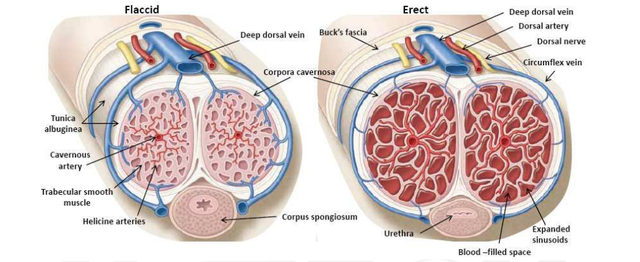
This is the male organ that deposits semen (containing sperm) inside a woman’s body during sexual intercourse. It contains two spongy masses of erectile tissue (the corpora cavernosa) on each side above the urethra.
- to manufacture the male gametes
- to deliver them to the site of fertilisation
Testicles (or testes)
Male gonads are called testicles. These two organs are composed of numerous coiled tubes (seminiferous tubules) where we find the cells that produce the spermatocytes (precursors of sperm cells). Additionally, it is in the testicles where the male hormone, testosterone, is produced and released in the bloodstream.
The testes are enclosed in a sac of skin called the scrotum, which hangs outside the body between the legs. This keeps them at a temperature 2-3 ºC lower than body temperature, best for development of the sperm.
The sperm is transported and stored in a series of tubes until it is released from the tip of the penis. These tubes are known as the reproductive ducts:
- Epididymis: Spermatocytes mature here becoming sperm (they are now ready for fertilisation). They now travel to the vas deferens.
- Sperm duct or vas deferens, which carries sperm from the testes to the urethra, passing by the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland on its way out.
- Urethra: Part of both the excretory and the reproductive system. This tube expels urine and seminal fluid from the body. (A valve prevents this happening at the same time!)
There are as well a number of glands that secrete substances that mix with the sperm to produce a fluid called semen.
- Seminal vesicle: This gland is responsible for adding nutrients (glucose) for the sperm.
- Prostate: Its function is to add liquids to the semen.
- Bulbourethral gland/Cowper's gland: This gland adds a clear liquid to the urethra just before ejaculation known as the pre-ejaculate. Its function is to clean and lubricate the urethra and prepare it for the semen to pass through.
Penis
This is the male organ that deposits semen (containing sperm) inside a woman’s body during sexual intercourse. It contains two spongy masses of erectile tissue (the corpora cavernosa) on each side above the urethra.
Female reproductive system
In addition to producing female gametes, the female reproductive system receives male gametes. It provides a site for fertilization and for the development of the zygote.
|
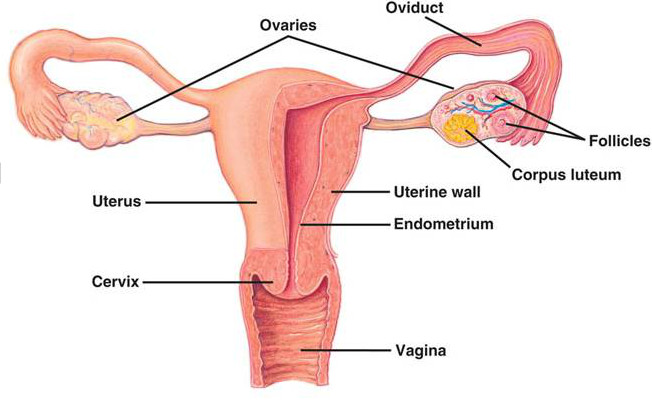
Ovaries
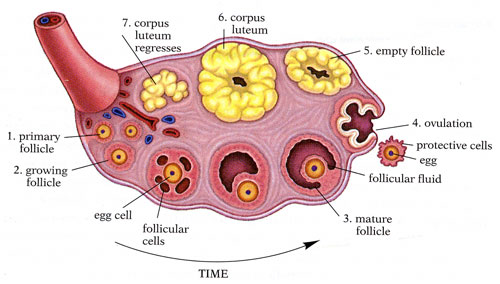
Female gonads are called ovaries. They are two of them found in the abdominal cavity (one on each side). The ovaries contain follicles which develop the ova. Once a month an ovum is released as a reaction to different hormonal levels (see menstrual cycle). The ovary also produces female sex hormones; oestrogen and progesterone |
The reproductive ducts in females play a role in fertilisation and gestation:
Fallopian tubes (oviduct): Carries the ovum to the uterus. Fertilisation occurs in the first third of the fallopian tube.
Uterus (womb): This is where the fetus develops; gestation. During pregnancy the uterus increases its size from 10 cm3 to 5 dm3. The wall of the uterus has a thick muscular layer (myometrium) lined with a mucus membrane (endometrium). The uterus narrows at its bottom, the cervix (also known as the neck of the uterus, where it is connected to the vagina.
Vagina or birth canal: This is an elastic, muscular canal with a soft, flexible lining that provides lubrication and sensation. The vagina receives the penis during intercourse, and also serves as a conduit for menstrual flow from the uterus. During childbirth, the vagina is the ‘way out’ for the baby.
Vulva: This is the external female sex organ, made of two lip-like folds of skin on each side of the vaginal opening: First the labia minora and then the labia majora. In between them is the clitoris, a sensitive organ with erectile tissue similar to that of the penis.
Fallopian tubes (oviduct): Carries the ovum to the uterus. Fertilisation occurs in the first third of the fallopian tube.
Uterus (womb): This is where the fetus develops; gestation. During pregnancy the uterus increases its size from 10 cm3 to 5 dm3. The wall of the uterus has a thick muscular layer (myometrium) lined with a mucus membrane (endometrium). The uterus narrows at its bottom, the cervix (also known as the neck of the uterus, where it is connected to the vagina.
Vagina or birth canal: This is an elastic, muscular canal with a soft, flexible lining that provides lubrication and sensation. The vagina receives the penis during intercourse, and also serves as a conduit for menstrual flow from the uterus. During childbirth, the vagina is the ‘way out’ for the baby.
Vulva: This is the external female sex organ, made of two lip-like folds of skin on each side of the vaginal opening: First the labia minora and then the labia majora. In between them is the clitoris, a sensitive organ with erectile tissue similar to that of the penis.
Some animations
The pill and the menstrual cycle
The pill and the menstrual cycle
References
Anon, (2015). [online] Available at: http://4.bp.blogspot.com/- [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Anon, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://U1eDEukP0fA/VJkkldS8tjI/AAAAAAAAAV8/4swpyYXpoV8/s1600/menstrual%2Bcycl e%2Bchart%2B-%2B3.jpeg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Artificialinsemination.files.wordpress.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
https://artificialinsemination.files.wordpress.com/2011/04/ovary-schematic.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Cabrera Calero, A. & Sanz Esteban, M. (2011). Biología y geología, 3º ESO, Andalucía. San Fernando de Henares, Madrid: Oxford Educación.
Cycles, F. (2015). Follow the Female Ovarian and Menstrual Cycles - For Dummies. [online] Dummies.com. Available at: http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/followthefemaleovarian-and-menstrual-cycles.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Dynamisch.nu, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://dynamisch.nu/feno/afbembryoengels/83ovary.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Healthline.com, (2015). Bulbourethral Gland (Cowper's Gland) Anatomy, Function & Diagram | Body Maps. [online] Available at: http://www.healthline.com/humanbodymaps/bulbourethralcowpers-gland [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Ibbio.pbworks.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://ibbio.pbworks.com/f/1317538698/oocyte.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Img.gawkerassets.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://img.gawkerassets.com/img/19d5bsdvffcvtpng/ku-xlarge.png [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Meritnation.com, (2016). Meritnation: The No.1 Education Site with Study Material & Live Classes for CBSE, ICSE, CPT, IITJEE, AIPMT & more. [online] Available at: http://www.meritnation.com/ [Accessed 5 Feb. 2016].
Nlm.nih.gov, (2015). Sexually Transmitted Diseases: MedlinePlus. [online] Available at:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/sexuallytransmitteddiseases.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Passmyexams.co.uk, (2015). Components of Blood, Cardiovascular System - Pass My Exams:
Easy exam revision notes for GSCE Biology. [online] Available at:
http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/biology/cardiovascular-system.html#1 [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Passmyexams.co.uk, (2015). The Menstrual Cycle - Pass My Exams: Easy exam revision notes for GSCE Biology. [online] Available at:
http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/biology/menstrual-cycle-and-hormones.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Pearltrees.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://www.pearltrees.com/s/pic/or/veinsarteriescapillaries-56549509 [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Pickering, W. (2006). Complete biology for IGCSE. Oxford [England]: Oxford University Press.
Tpsbiology11student2.wikispaces.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://tpsbiology11student2.wikispaces.com/file/view/bloodcomponents.jpg/186793981/bloo dcomponents.jpg [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Urgo.co.uk, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://www.urgo.co.uk/uploadedfiles/img/images/venous-system-big-01.jpg [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Webmd.com, (2015). The Vagina (Human Anatomy): Picture, Parts, Function, Definition, and Problems. [online] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/women/picture-of-the-vagina [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Women-info.com, (2016). [online] Available at: http://www.women-info.com/ [Accessed 5 Feb.
2016].
Anon, (2015). [online] Available at: http://4.bp.blogspot.com/- [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Anon, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://U1eDEukP0fA/VJkkldS8tjI/AAAAAAAAAV8/4swpyYXpoV8/s1600/menstrual%2Bcycl e%2Bchart%2B-%2B3.jpeg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Artificialinsemination.files.wordpress.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
https://artificialinsemination.files.wordpress.com/2011/04/ovary-schematic.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Cabrera Calero, A. & Sanz Esteban, M. (2011). Biología y geología, 3º ESO, Andalucía. San Fernando de Henares, Madrid: Oxford Educación.
Cycles, F. (2015). Follow the Female Ovarian and Menstrual Cycles - For Dummies. [online] Dummies.com. Available at: http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/followthefemaleovarian-and-menstrual-cycles.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Dynamisch.nu, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://dynamisch.nu/feno/afbembryoengels/83ovary.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Healthline.com, (2015). Bulbourethral Gland (Cowper's Gland) Anatomy, Function & Diagram | Body Maps. [online] Available at: http://www.healthline.com/humanbodymaps/bulbourethralcowpers-gland [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Ibbio.pbworks.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://ibbio.pbworks.com/f/1317538698/oocyte.jpg [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Img.gawkerassets.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://img.gawkerassets.com/img/19d5bsdvffcvtpng/ku-xlarge.png [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Meritnation.com, (2016). Meritnation: The No.1 Education Site with Study Material & Live Classes for CBSE, ICSE, CPT, IITJEE, AIPMT & more. [online] Available at: http://www.meritnation.com/ [Accessed 5 Feb. 2016].
Nlm.nih.gov, (2015). Sexually Transmitted Diseases: MedlinePlus. [online] Available at:
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/sexuallytransmitteddiseases.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Passmyexams.co.uk, (2015). Components of Blood, Cardiovascular System - Pass My Exams:
Easy exam revision notes for GSCE Biology. [online] Available at:
http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/biology/cardiovascular-system.html#1 [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Passmyexams.co.uk, (2015). The Menstrual Cycle - Pass My Exams: Easy exam revision notes for GSCE Biology. [online] Available at:
http://www.passmyexams.co.uk/GCSE/biology/menstrual-cycle-and-hormones.html [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Pearltrees.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://www.pearltrees.com/s/pic/or/veinsarteriescapillaries-56549509 [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Pickering, W. (2006). Complete biology for IGCSE. Oxford [England]: Oxford University Press.
Tpsbiology11student2.wikispaces.com, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://tpsbiology11student2.wikispaces.com/file/view/bloodcomponents.jpg/186793981/bloo dcomponents.jpg [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Urgo.co.uk, (2015). [online] Available at:
http://www.urgo.co.uk/uploadedfiles/img/images/venous-system-big-01.jpg [Accessed 4 May 2015].
Webmd.com, (2015). The Vagina (Human Anatomy): Picture, Parts, Function, Definition, and Problems. [online] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/women/picture-of-the-vagina [Accessed 10 May 2015].
Women-info.com, (2016). [online] Available at: http://www.women-info.com/ [Accessed 5 Feb.
2016].