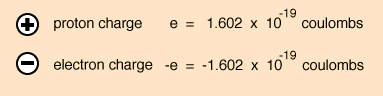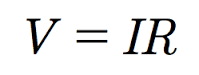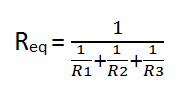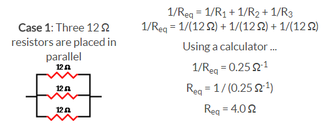Unit 8 - Electricity
|
Key concept - Change- Past of an object in motion can be reconstructed and future foreseen on the basis of the current state and the forces acting upon it
Related concepts - Patterns and Motion- Motion and forces can be expressed in mathematical equations Global concept - Scientific and Technical Innovation- Constant parallel improvement of science and technology can provide answers to some of human questions about the universe.. |
Key words:
|
|
|
Pre-knowledge - Drawing circuits
8a - What is electric charge?
You may remember from Unit 6 (redox) that Faraday´s constant shows the charge of 1 mol of electrons --> 96500 C
8b - Static electricity
Static electricity is the build up of electrical charge on an object. This is commonly done via the "rubbing" or repeated contact between 2 materials. VIDEO
|
What causes it? Static charge builds up when one material has a greater electron affinity than another. When rubbed against another material, it can steal electrons from it leading to an excess of negative charge on one item and positive charge on the other.
When the hair of the baby becomes charged, the strands of hair spread apart as the like charges repel each other.
|
|
|
|
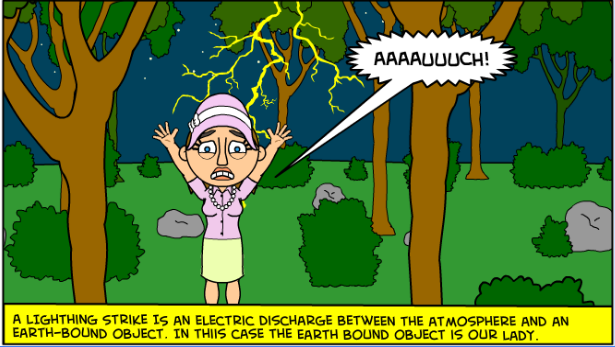
When the number of electrons reaches a certain point, the forces of repulsion become great enough for the electrons to try and jumps away from the material to form electrostatic equilibrium again.
This is called an electrostatic discharge. A large example is that of lightning. |
|
Task 8b:
1. Describe what is seen between same and opposite forces. 2. Explain the following phenomenon:
|
8c - Ohm´s law
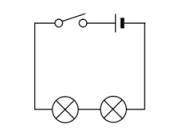
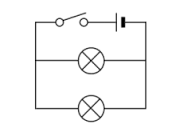
To be able to use Ohm´s law correctly we must consider whether a circuit is in series or in parallel:
8ci - Current
Dealing with current in series and parallel
8cii - Resistance
Dealing with resistance in series and parallel
|
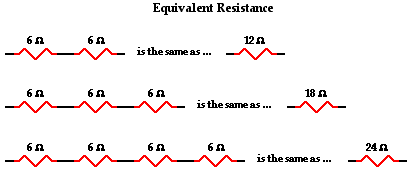
Series: To calculate the equivalent resistance in a circuit, we simply sum the values of each resistor in the circuit.
Req = R1 + R2 + R3... |
Parallel: To calculate the equivalent resistance (Req) caused by the different resistors.
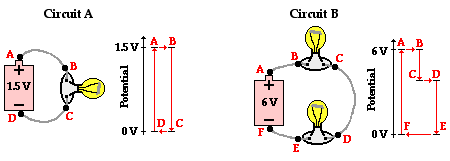
8cii - Voltage
8d - Consequences of electricity use
|
The majority of the production of electricity comes from the burning of fossil fuels as shown to the right. The act of retrieving fossil fuels and the products of burning them are responsible for many global issues.
|
Revision
1. Ohm´s law problems (remember that "potential difference" is another word for "voltage")
2. Ohm´s law problems
|
| ||||