Unit 3a Living things
Click here for the activity
Key concept - Relationships- How do different organisms interact on Earth?
Related concepts - Interaction and Balance - Try to imagine how the living things you learn about interact with each other and how changes in one part of the web of life can affect the overall balance of an ecosystem.
Global concept - Scientific and technical innovation - Do you think Science and Technology is causing changes in our world? Or can it be used to help solve environmental problems?
Related concepts - Interaction and Balance - Try to imagine how the living things you learn about interact with each other and how changes in one part of the web of life can affect the overall balance of an ecosystem.
Global concept - Scientific and technical innovation - Do you think Science and Technology is causing changes in our world? Or can it be used to help solve environmental problems?
Unit 3 KEYWORDS Click here for the activity
|
|
|
Task guide
The tasks and questions on the Weebly will be coloured to represent the different style of questions that you will find in your exams. The task should be completed in your "Natural Sciences" GoogleDrive document.
Green - Stating scientific knowledge
Orange - Applying scientific knowledge and understanding
Red - Analysing and evaluating information
There will also be "extension" tasks for students who finish tasks quickly! Also look out for links to interactive resources and videos.
The tasks and questions on the Weebly will be coloured to represent the different style of questions that you will find in your exams. The task should be completed in your "Natural Sciences" GoogleDrive document.
Green - Stating scientific knowledge
Orange - Applying scientific knowledge and understanding
Red - Analysing and evaluating information
There will also be "extension" tasks for students who finish tasks quickly! Also look out for links to interactive resources and videos.
Living Things
Task 3a:
In your "Natural Sciences" Word (NSD) document copy and paste the sentence below and then complete the task:
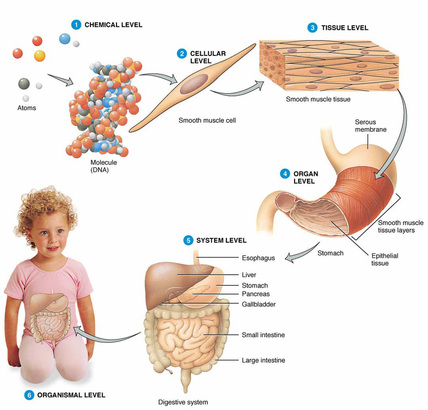
All living things have different levels of organisation so they can perform the characteristics of life.
We can also organise living things into different categories so that we can study and talk about them more easily.
Copy this diagram in Google Drawings and complete the boxes to show the organisation of living things. Then paste it into your NSD under a suitable heating.
In your "Natural Sciences" Word (NSD) document copy and paste the sentence below and then complete the task:
All living things have different levels of organisation so they can perform the characteristics of life.
We can also organise living things into different categories so that we can study and talk about them more easily.
Copy this diagram in Google Drawings and complete the boxes to show the organisation of living things. Then paste it into your NSD under a suitable heating.
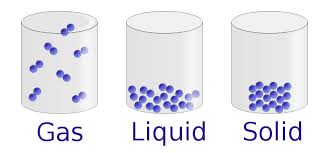
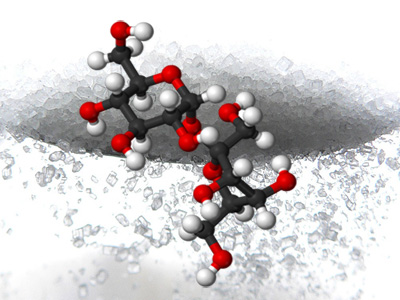
All the life that we know of is based on one particular element: Carbon. Any molecule that contains carbon is known as an organic molecule. Elements are the building blocks of matter (See Unit 5), and when they are joined together, we call these molecules. Molecules are what you think about vibrating and moving in the different states of matter:
Wikimedia (2015)
Can you remember this song?
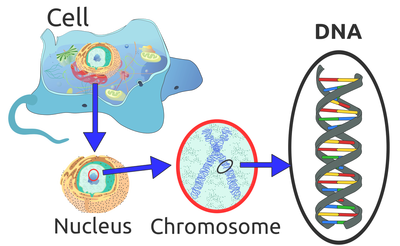
We can extend the organisation diagram to include what the cells of living things are made of: Biomolecules.
Update your diagram to include Biomolecules.
Can you remember this song?
We can extend the organisation diagram to include what the cells of living things are made of: Biomolecules.
Update your diagram to include Biomolecules.
Other bioelements
Other important elements that can be found in living things include: carbon (C), hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), phosphorous (P) and sulfur (S). These elements make up over 99% of the mass of all living things (Barrio Gómez de Agüero, 2011). You can remember them as CHONPS.
Task 3b:
In your NSD, insert a 5 x 3 table with the 4 different biomolecules, their function and a picture example of each. Don´t forget to reference where you find the information and pictures!
[Hint: Use this website to help you format the reference properly by changing the "citation style" to APA]
In your NSD, insert a 5 x 3 table with the 4 different biomolecules, their function and a picture example of each. Don´t forget to reference where you find the information and pictures!
[Hint: Use this website to help you format the reference properly by changing the "citation style" to APA]
Living things are also made of inorganic compounds, the main one being water.
Plants are up to 80% water and you are up to 90% water!
(Barrio Gómez de Agüero, 2011).
Check your Learning
Without looking at the diagrams, can you say the levels of organisation backwards?
What do all living things do?
What similarities can you find between the following organisms?
The above organisms may look very different, but they all:
Can you remember the scientific words for these 3 Vital Functions?
Task 3c:
Find the 3 vital functions in the key-words section at the top of the page and make an entry in your NSD describing the meaning of each term. Copy and paste the following sentence under your heading, before your list:
All living things perform three vital functions, they are:
You can use this website to help you check the meanings, but write them in your own words. When you have finished, watch the following video:
- Get food
- Respond to changes in their environment
- Produce new living things
Can you remember the scientific words for these 3 Vital Functions?
Task 3c:
Find the 3 vital functions in the key-words section at the top of the page and make an entry in your NSD describing the meaning of each term. Copy and paste the following sentence under your heading, before your list:
All living things perform three vital functions, they are:
You can use this website to help you check the meanings, but write them in your own words. When you have finished, watch the following video:
(Bioweb.uwlax.edu, 2015)
The Cell and Cell Theory
Look at your finger, can you see the cells you are made of? It took a long time for people to discover what the building blocks of all living things are. Cells are complex structures that are formed from organic and inorganic compounds. A cell performs the three vital functions that characterise life.
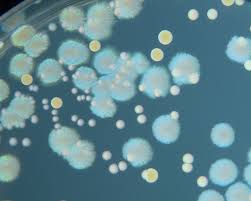
A living thing can be made of an individual cell (single-cell organism), like bacteria, or from many cells (multicellular organism), like you! Watch the two videos below to discover what structures make up cells and how we know they exist:
A living thing can be made of an individual cell (single-cell organism), like bacteria, or from many cells (multicellular organism), like you! Watch the two videos below to discover what structures make up cells and how we know they exist:
|
|
|
Task 3d:
Write a heading in your NSD and copy and paste the following sentence:
Cells are the building blocks of all living things are. Cells are complex structures that are formed from organic and inorganic compounds. A cell performs the three vital functions that characterise life.
A living thing can be made of an individual cell (single-cell organism), like bacteria, or from many cells (multicellular organism), like .................................. .
Use the internet to write a definition for each of the following:
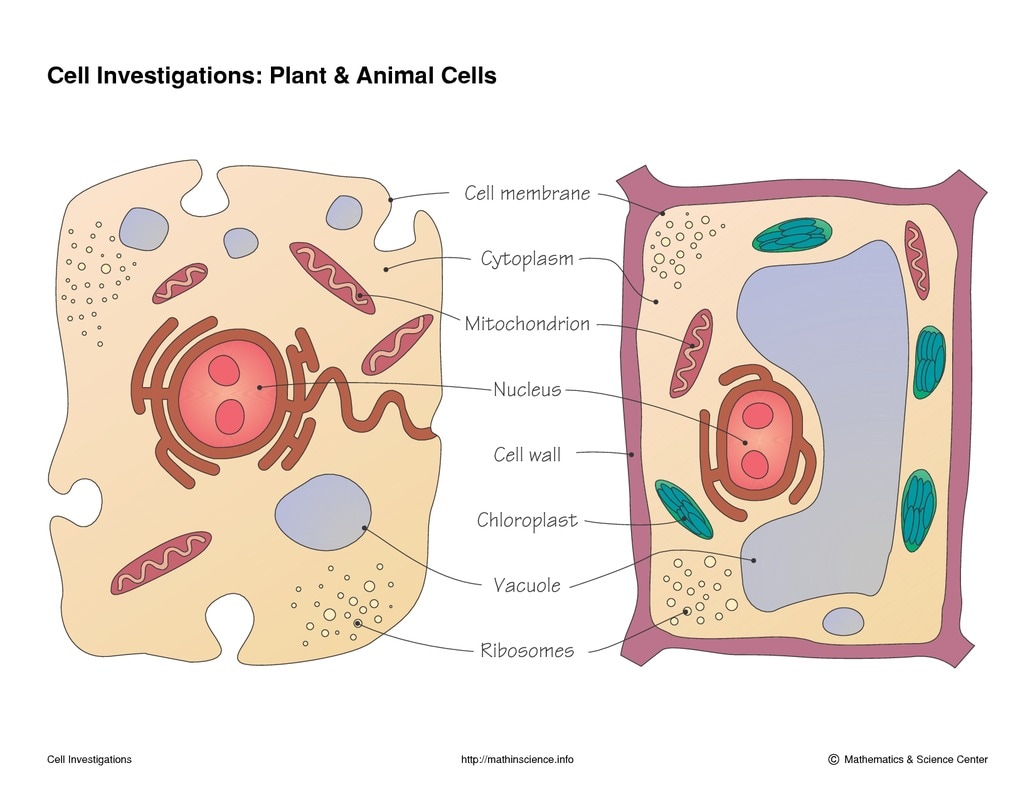
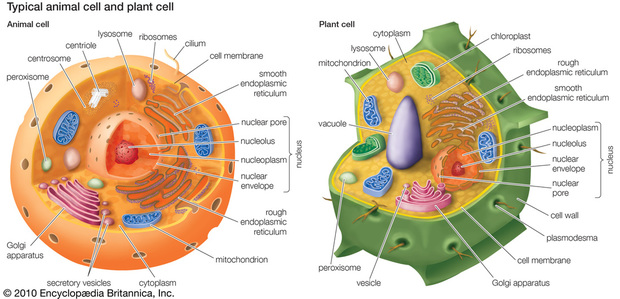
Copy this diagram of a plant and animal cell into your NSD. Describe the main differences between the two?
Write a heading in your NSD and copy and paste the following sentence:
Cells are the building blocks of all living things are. Cells are complex structures that are formed from organic and inorganic compounds. A cell performs the three vital functions that characterise life.
A living thing can be made of an individual cell (single-cell organism), like bacteria, or from many cells (multicellular organism), like .................................. .
Use the internet to write a definition for each of the following:
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Organelles
- Mitochondria
Copy this diagram of a plant and animal cell into your NSD. Describe the main differences between the two?
(BBC.co.uk, 2015)
Extension: Write a summary of the differences under the diagram.
[Don´t forget to include the complete reference your NSD.]
[Don´t forget to include the complete reference your NSD.]
Make sure you can correctly label a cell diagram in an exam. You can practice by following this link.
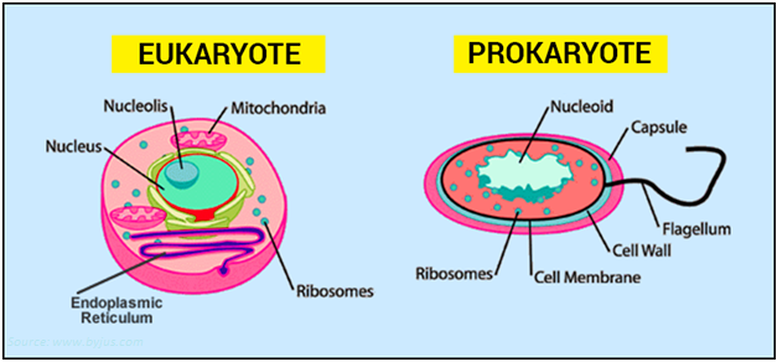
Types of Cells
Explore!
Use the following websites to explore the different types of cells:
Task 3e:
1. In your NSD under a suitable heading, find, insert and reference two pictures of a prokaryotic cell and two of a eukaryotic cell. Can you find one diagram and one as seen through a microscope for each?
2. Complete the following sentences by copying the text by using Ctrl+C, and pasting it into your NSD with Ctrl+V. Then delete the incorrect words.
a) Prokaryotic cells have / do not have a true nucleus.
b) Prokaryotic cells are more / less primitive than eukaryotic cells.
c) Eukaryotic cells have / do not have a true nucleus.
d) Eukaryotic cells can / cannot be a plant or animal cell.
3. Copy and paste the following table. Complete the tables by saying if the features are present or not in the the different types of cells.
1. In your NSD under a suitable heading, find, insert and reference two pictures of a prokaryotic cell and two of a eukaryotic cell. Can you find one diagram and one as seen through a microscope for each?
2. Complete the following sentences by copying the text by using Ctrl+C, and pasting it into your NSD with Ctrl+V. Then delete the incorrect words.
a) Prokaryotic cells have / do not have a true nucleus.
b) Prokaryotic cells are more / less primitive than eukaryotic cells.
c) Eukaryotic cells have / do not have a true nucleus.
d) Eukaryotic cells can / cannot be a plant or animal cell.
3. Copy and paste the following table. Complete the tables by saying if the features are present or not in the the different types of cells.
Feature |
Prokaryotes |
Eukaryotes |
DNA |
- |
- |
Cytoplasm |
- |
- |
Cell membrane |
- |
- |
Nucleus |
- |
- |
Organelles |
- |
- |
How do you get your food?
We divide living things into two groups, depending on how they get their food. It depends on whether they make their own food: Autotrophs, or if they eat other organisms: Heterotrophs.
Most autotrophs use the energy in sunlight to produce glucose. Examples include plants, algae and some bacteria.
Most autotrophs use the energy in sunlight to produce glucose. Examples include plants, algae and some bacteria.
|
|
|
Heterotrophs obtain nutrients from other living things. They can be carnivores, herbivores or omnivores.
Task 3f:
Write an entry in your NSD about the two different types of Nutrition. Use this website to help you and make sure you define the terms carnivores, herbivores and omnivores.
Task 3f:
Write an entry in your NSD about the two different types of Nutrition. Use this website to help you and make sure you define the terms carnivores, herbivores and omnivores.
|
The importance of Plants
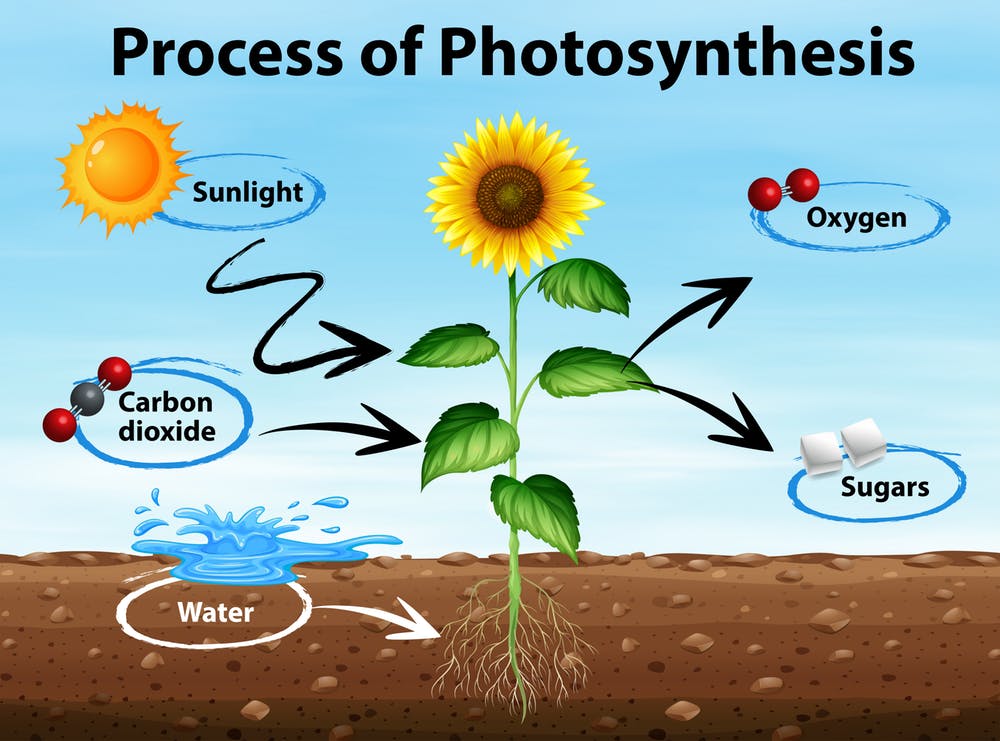
Animals need to eat food to get their energy. But green plants and algae do not. Instead they make their own food in a process called photosynthesis. Almost all life on Earth depends upon this process. Photosynthesis is also important in maintaining the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. These are the things that plants need for photosynthesis:
These are the things that plants make by photosynthesis:
The oxygen produced is released into the air from the leaves. The glucose produced can be turned into other substances, such as starch and plant oils, which are used as an energy store. This energy can be released by respiration. |
|
Task 3g
1. Write the equation for photosynthesis and respiration. What is the relationship between these two processes? 2. When do plants do photosynthesis and when do they do respiration? 3. Complete the table for photosynthesis and respiration. EXTENSION 4. When people go on a diet or exercise to lose weight, they are trying to reduce their mass. In what form is their mass being lost? |
|
References
Barrio Gómez de Agüero, J. (2011). Natural sciences, ESO 1. [San Fernando de Henares, Madrid]: Oxford Educación.
BBC.co.uk,. (2015). BBC - GCSE Bitesize: Animal and plant cells. Retrieved 30 June 2015, from http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/add_aqa_pre_2011/cells/cells1.shtml
Chadwick, N. (2015). An Algae covered pond (C) N Chadwick :: Geograph Britain and Ireland.Geograph.org.uk. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://www.geograph.org.uk/photo/1963014
Gaffney, A. (2011). Characteristics of the Five Kingdoms. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bEk-3fvutMc&index=4&list=PLvuHqrfWeC63Q348MA-N86nw7PghHN9se
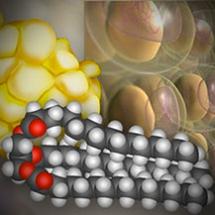
HHMI.org,. (2015). Molecular Structure of Fat | HHMI's BioInteractive. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/molecular-structure-fat
Keratinresearch.com,. (2015). INVERTO Keratin Hair Treatment. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://www.keratinresearch.com/index.php/what-is-inverto.html/
Public Radio International,. (2015). New research on plant intelligence may forever change how you think about plants. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://www.pri.org/stories/2014-01-09/new-research-plant-intelligence-may-forever-change-how-you-think-about-plants
Sciencelearn Hub,. (2015). DNA, chromosomes and gene expression. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://sciencelearn.org.nz/Contexts/Uniquely-Me/Science-Ideas-and-Concepts/DNA-chromosomes-and-gene-expression
uiuc.edu,. (2015). Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://butane.chem.uiuc.edu/pshapley/GenChem2/B4/book.pdf
Upload.wikimedia.org,. (2015). Retrieved 26 June 2015, from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/89/States_of_matter_En.svg/734px-States_of_matter_En.svg.png.
WildAid,. (2015). Elephants. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://wildaid.org/elephants
Barrio Gómez de Agüero, J. (2011). Natural sciences, ESO 1. [San Fernando de Henares, Madrid]: Oxford Educación.
BBC.co.uk,. (2015). BBC - GCSE Bitesize: Animal and plant cells. Retrieved 30 June 2015, from http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/add_aqa_pre_2011/cells/cells1.shtml
Chadwick, N. (2015). An Algae covered pond (C) N Chadwick :: Geograph Britain and Ireland.Geograph.org.uk. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://www.geograph.org.uk/photo/1963014
Gaffney, A. (2011). Characteristics of the Five Kingdoms. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bEk-3fvutMc&index=4&list=PLvuHqrfWeC63Q348MA-N86nw7PghHN9se
HHMI.org,. (2015). Molecular Structure of Fat | HHMI's BioInteractive. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/molecular-structure-fat
Keratinresearch.com,. (2015). INVERTO Keratin Hair Treatment. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://www.keratinresearch.com/index.php/what-is-inverto.html/
Public Radio International,. (2015). New research on plant intelligence may forever change how you think about plants. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://www.pri.org/stories/2014-01-09/new-research-plant-intelligence-may-forever-change-how-you-think-about-plants
Sciencelearn Hub,. (2015). DNA, chromosomes and gene expression. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://sciencelearn.org.nz/Contexts/Uniquely-Me/Science-Ideas-and-Concepts/DNA-chromosomes-and-gene-expression
uiuc.edu,. (2015). Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://butane.chem.uiuc.edu/pshapley/GenChem2/B4/book.pdf
Upload.wikimedia.org,. (2015). Retrieved 26 June 2015, from https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/89/States_of_matter_En.svg/734px-States_of_matter_En.svg.png.
WildAid,. (2015). Elephants. Retrieved 29 June 2015, from http://wildaid.org/elephants