Kingdom Animalia
Keywords
|
|
|
|
All animals are multicellular organisms with real tissues and heterotrophic nutrition
Members of the animal kingdom can be divided into two large groups based on whether they have a backbone as part of a bony skeleton. The backbone is made up of separate bones called vertebrae, which allow these animals to move with great ease.
Invertebrates -Animals that do not have a backbone (spine, vertebral column). However, they can have an internal or external skeleton (exoskeleton) of some sort. In any case, such skeleton is always much simpler than those of vertebrates and never made up of bones.
Vertebrates - Animals that have a hard, usually bony, internal skeleton with a backbone.
Members of the animal kingdom can be divided into two large groups based on whether they have a backbone as part of a bony skeleton. The backbone is made up of separate bones called vertebrae, which allow these animals to move with great ease.
Invertebrates -Animals that do not have a backbone (spine, vertebral column). However, they can have an internal or external skeleton (exoskeleton) of some sort. In any case, such skeleton is always much simpler than those of vertebrates and never made up of bones.
Vertebrates - Animals that have a hard, usually bony, internal skeleton with a backbone.
INVERTEBRATES
We can classify the group of invertebrates into 6 groups: poriferans, cnidarian, worms, echinoderms, molluscs and arthropods.
I. Poriferans.- the simplest animals.
Because of their appearance and their lack of movement, sponges hardly seem to be animals. However, they are indeed the most primitive animals. We say they are the most primitive animals because they do not have organs. Sponges are aquatic creatures, the majority being sea sponges that stick to rocks on the sea bed, plants or corals.
I. Poriferans.- the simplest animals.
Because of their appearance and their lack of movement, sponges hardly seem to be animals. However, they are indeed the most primitive animals. We say they are the most primitive animals because they do not have organs. Sponges are aquatic creatures, the majority being sea sponges that stick to rocks on the sea bed, plants or corals.
Poriferans or sponges have soft porous bodies, shaped like a sack, with an internal cavity, the atrial cavity, which is opened at the top by a larger pore named oscule.
They eat and breathe thanks to the water that comes in through their microscopic pores, and circulates through their body, to finally exit through the oscule. From this water current, sponges take small living beings and dissolved oxygen.
Sponges can reproduce sexually and asexually.
Sponges can reproduce sexually and asexually.
II. Cnidarians.- jellyfish, corals and sea anemones.
Cnidarians are aquatic animals with soft, sack-like, translucent bodies.
These animals are a little more developed than the sponges, presenting a few simple organs. Cnidarians have one opening that acts as both mouth and anus. This opening is usually surrounded with tentacles.
Some cnidarians, such as corals, stick to the sea beds, while others; such as jellyfish are creatures that swim.
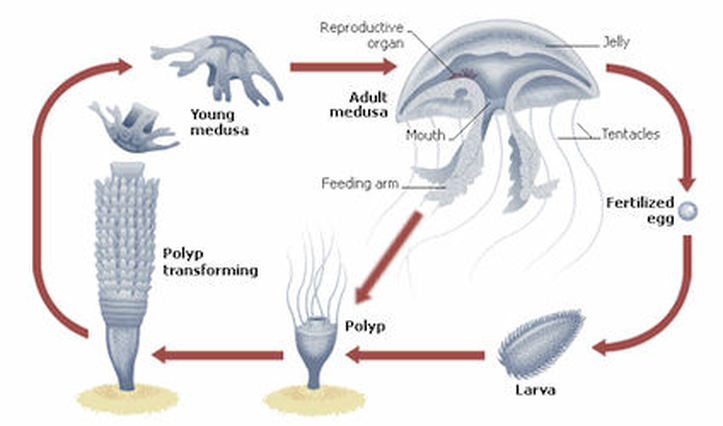
Cnidariancan have two stages in their life cycle: a polyp and a medusa. Polyps are always attached to the sea beds, while the medusa swims freely.
Medusas are formed inside the polyps and are released when this breaks (asexual reproduction). Medusas reproduce sexually, forming a larva that develops into a polyp.
Some cnidarians, such as corals, stick to the sea beds, while others; such as jellyfish are creatures that swim.
Cnidariancan have two stages in their life cycle: a polyp and a medusa. Polyps are always attached to the sea beds, while the medusa swims freely.
Medusas are formed inside the polyps and are released when this breaks (asexual reproduction). Medusas reproduce sexually, forming a larva that develops into a polyp.
|
|
|
Some cnidarians only exist in the form of a polyp and never produce medusas.
III. Worms, a large and diverse group.
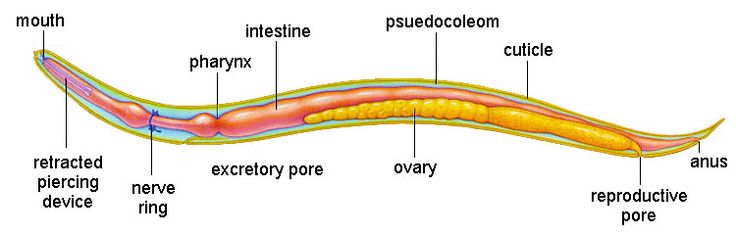
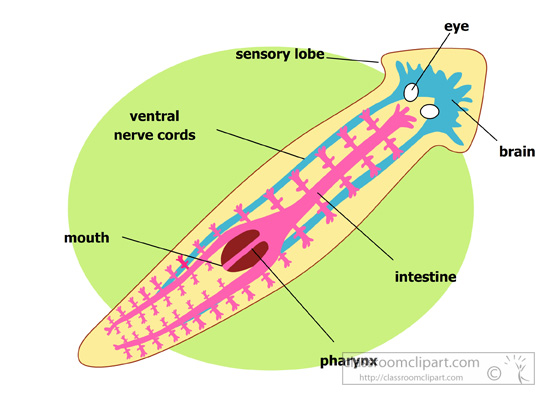
There are cylindrical worms, such as the earthworm, and flat worms such as planarians. Some worms are very simple organisms with few organs and apparatus, while others have quite a complex anatomy.
There are cylindrical worms, such as the earthworm, and flat worms such as planarians. Some worms are very simple organisms with few organs and apparatus, while others have quite a complex anatomy.
|
Worms breathe through their skin. Simplest worms don’t have a circulatory system, but the earthworms are the simplest animals to have a transport system with closed blood vessels. As mentioned earlier the simplest worms are missing certain organs and apparatus, while the most complex ones have well developed systems; such as the nervous system, reproduction system etc.
All worms reproduce sexually, and those simplest worms can also reproduce asexually through fragmentation. Parasites are the worms with the most complex life cycles. |
|
IV. Echinoderms.- from Greek, echino ‘spiny’ derma ‘skin’
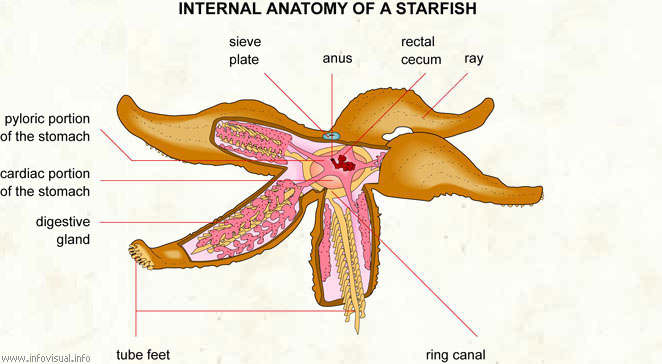
This group of invertebrates include starfish, sea urchins and sea cucumbers.
Echinoderms only live in marine ecosystems and they are all carnivores. Despite their delicate appearance, starfish are voracious predators.
They breathe through their skin, but a few have gills. Their reproduction is sexual and sometimes asexual through fragmentation. The larvae produced after fertilization are very different from the adult.
They also regenerate quite easily. If they lose an arm it may grow back, and the lost arm may grow into a complete individual.
This group of invertebrates include starfish, sea urchins and sea cucumbers.
Echinoderms only live in marine ecosystems and they are all carnivores. Despite their delicate appearance, starfish are voracious predators.
They breathe through their skin, but a few have gills. Their reproduction is sexual and sometimes asexual through fragmentation. The larvae produced after fertilization are very different from the adult.
They also regenerate quite easily. If they lose an arm it may grow back, and the lost arm may grow into a complete individual.
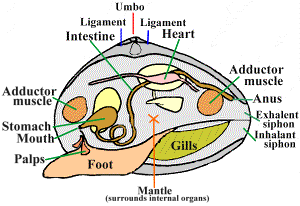
V. Molluscs
Molluscs are animals with soft bodies, which have a foot and a body. Most molluscs have a shell that protects their bodies.
Molluscs are animals with soft bodies, which have a foot and a body. Most molluscs have a shell that protects their bodies.
Most molluscs are aquatic creatures, only a few are terrestrial animals (snails and slugs) in which case they live in very humid areas.
Their way of nutrition varies from species to species. Some eat plants while others eat animals. All have a well-developed digestive system. They have a special tongue called radula, with lots of tiny teeth that helps them to obtain their food.
Terrestrial molluscs breathe through lungs, while aquatic molluscs have gills. Molluscs have a simple circulatory system; they have a heart and blood vessels. They also have primitive kidneys, which allow them to do carry on the excretion function. Their reproduction is always sexual, the female laying eggs, from which larvae come out.
There are three main groups within the molluscs: bivalves, gastropods and cephalopods.
Bivalves, meaning two valves, are aquatic animals. This group includes clams, cockles, oysters, scallops, and
mussels among others.
Their way of nutrition varies from species to species. Some eat plants while others eat animals. All have a well-developed digestive system. They have a special tongue called radula, with lots of tiny teeth that helps them to obtain their food.
Terrestrial molluscs breathe through lungs, while aquatic molluscs have gills. Molluscs have a simple circulatory system; they have a heart and blood vessels. They also have primitive kidneys, which allow them to do carry on the excretion function. Their reproduction is always sexual, the female laying eggs, from which larvae come out.
There are three main groups within the molluscs: bivalves, gastropods and cephalopods.
Bivalves, meaning two valves, are aquatic animals. This group includes clams, cockles, oysters, scallops, and
mussels among others.
|
Cephalopods are aquatic animals. Their name meaning “feet on their head” refers to the fact that the foot of these animals has evolved into tentacles that part from their head, surrounding the mouth. This group usually doesn’t have an external shell, but a small, hard internal piece instead. The nautilus is the only one that shows a well-developed shell. Other examples of cephalopods are squids, cuttlefish, and octopuses
|
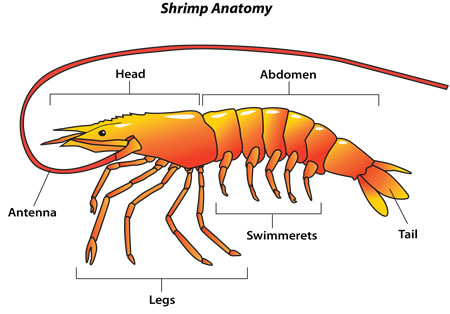
VI. Arthropods.- the largest and most diverse group of the animal kingdom.
The distinguishing feature of arthropods is the presence of a skeletal covering made up of jointed parts (appendages), and articulated legs. This shell covers and protects their bodies much like a suit of armour.
Their body is divided into the head, thorax, abdomen and extremities.
This is the largest group of the entire animal kingdom, with more than one million different species, most of them being insects. (about 90%)
As you could imagine, they are found in all different habitats and all types of ecosystems. They swim, walk and fly (depending on the species) Their nutrition is quite diverse as well. Some are herbivores, some carnivores and others are scavengers (eat dead organisms in decomposition). All arthropods present mouth parts.
Terrestrial arthropods breathe through tracheae (air tubes) or special lungs (book lungs), and aquatic arthropods through gills.
They have one long blood vessel along their back (dorsal circulatory system). A portion of this vessel widens becoming the heart.
Their excretory system is quite simple. Arthropods all have sexual reproduction (two sexes usually separate) with internal fertilization and the female lays eggs. Some larvae will undergo a process known as metamorphosis.
This is the largest group of the entire animal kingdom, with more than one million different species, most of them being insects. (about 90%)
As you could imagine, they are found in all different habitats and all types of ecosystems. They swim, walk and fly (depending on the species) Their nutrition is quite diverse as well. Some are herbivores, some carnivores and others are scavengers (eat dead organisms in decomposition). All arthropods present mouth parts.
Terrestrial arthropods breathe through tracheae (air tubes) or special lungs (book lungs), and aquatic arthropods through gills.
They have one long blood vessel along their back (dorsal circulatory system). A portion of this vessel widens becoming the heart.
Their excretory system is quite simple. Arthropods all have sexual reproduction (two sexes usually separate) with internal fertilization and the female lays eggs. Some larvae will undergo a process known as metamorphosis.
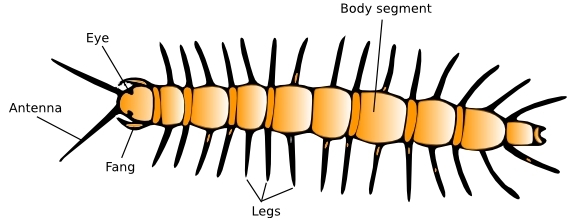
Myriapods (millipedes, centipedes)
Terrestrial arthropods. They have long, thin bodies divided into many segments, with pairs of legs in each one of these segments.
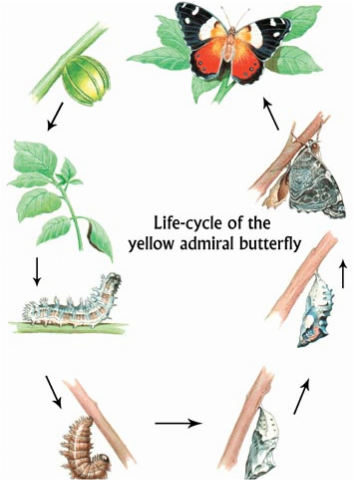
Insects (beetles, butterflies, flies, ants…)
Terrestrial and fresh water animals. They have distinct head, thorax and abdomen, two antennae, 6 legs and 4 wings. In the head they have the eyes and the antennae, and in the thorax the wings and legs.
Since this is such a large and varied group, their nutrition is also quite different from one type to another.
They all have sexual reproduction. Some present metamorphosis in their development, in which case the adult insect is very different from the larva.
· Process of metamorphosis.
Terrestrial arthropods. They have long, thin bodies divided into many segments, with pairs of legs in each one of these segments.
Insects (beetles, butterflies, flies, ants…)
Terrestrial and fresh water animals. They have distinct head, thorax and abdomen, two antennae, 6 legs and 4 wings. In the head they have the eyes and the antennae, and in the thorax the wings and legs.
Since this is such a large and varied group, their nutrition is also quite different from one type to another.
They all have sexual reproduction. Some present metamorphosis in their development, in which case the adult insect is very different from the larva.
· Process of metamorphosis.
|
1.From the egg we get a larva, whose physical appearance is that of a worm. The larva eats and grows until it reaches the following stage.
2. The pupa stage.- its skin hardens, and lots of changes take place inside it. Some times they are enclosed is a cocoon or chrysalid.(chrysalis) 3. Finally the pupa opens up and the adult insect comes out of it. |
Vertebrate Animals
Vertebrates à animals that have an internal skeleton (endoskeleton) with a backbone. The skeleton can be made up of bones (hard) or made up of cartilage (more flexible). The endoskeleton in some vertebrates is a combination of bones and cartilage. Vertebrates also show a complex nervous system and a well developed brain.
The endoskeleton of vertebrates holds the organs of the animal, and gives some sort of shape to the body.
In the five groups of vertebrates we can see gradual adaptations to life on land.
There are five groups of vertebrates: fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Out of these five groups, fish, amphibians and reptiles are cold-blooded animals or poikilotherms. The body temperature of these animals is dependent upon their environment. (it changes as the temperature in their surrounding changes) Birds and mammals are warm-blooded animals or homoiotherms. These two groups can generate and maintain a constant body temperature regardless of the outside temperature.
I. Fish.-
In the five groups of vertebrates we can see gradual adaptations to life on land.
There are five groups of vertebrates: fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Out of these five groups, fish, amphibians and reptiles are cold-blooded animals or poikilotherms. The body temperature of these animals is dependent upon their environment. (it changes as the temperature in their surrounding changes) Birds and mammals are warm-blooded animals or homoiotherms. These two groups can generate and maintain a constant body temperature regardless of the outside temperature.
I. Fish.-
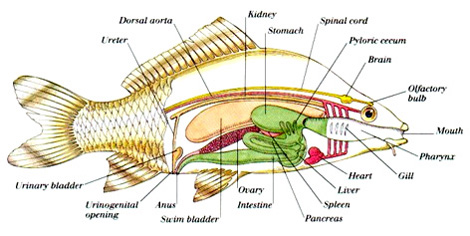
Aquatic, cold-blooded or poikilotherm vertebrates. They have fins for movement in the back and thorax (dorsal fins), stomach (ventral fins), and tail (caudal fin). Their skin is covered with scales. The majority are oviparous.
Fish breathe through gills. The gills are located behind the mouth and protected by the operculum. Their heart has two chambers (ventricle and auricle)
Some fish live in the sea, such as the hake, sharks, etc. and others in fresh water, like the trout.
Most fish are oviparous, with external fertilization; however, a few fish, such most sharks and rays are ovoviviparous (internal fertilization).
Most fish have a bony skeleton, but there are some species which have a cartilagenous
skeleton (such as sharks and rays,).
The nutrition among the different species of this group is quite varied. Some eat algae, others eat crustaceans, others small animals etc.
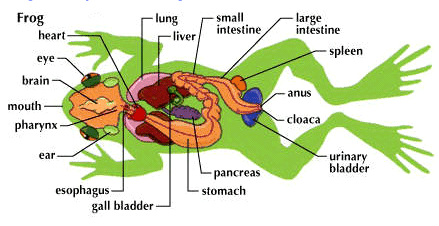
II. Amphibians.- (includes frogs, toads, newts(tritons), and salamanders)
Cold-blooded or poikilotherm animals which spend a big part of their lives in the water. The adults spend much of their life in land but the female always goes back to water to lay her eggs.
The skin of these vertebrates has mucus glands to maintain it humid and slippery, and some species also have poisonous glands in the skin as a protective measure against predators. Their heart has two auricles and one ventricle.
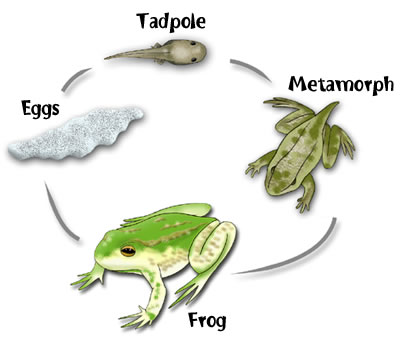
Amphibians reproduce sexually with external fertilization. The female lays the eggs in the water (female and male get together to copulate, but there is not internal fertilization. The only reason for getting together is to make sure that the majority of the eggs are fertilized)
From eggs we get larvae, which turn into tadpoles, which undergo metamorphosis.
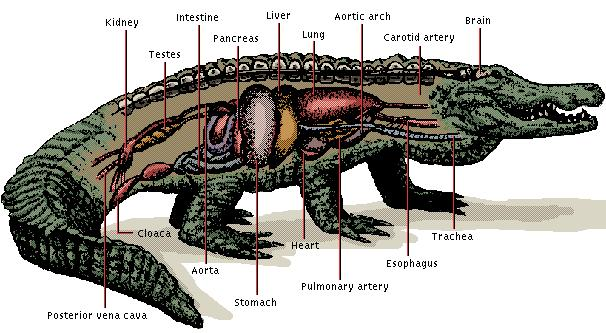
III. Reptiles.-
Amphibians reproduce sexually with external fertilization. The female lays the eggs in the water (female and male get together to copulate, but there is not internal fertilization. The only reason for getting together is to make sure that the majority of the eggs are fertilized)
From eggs we get larvae, which turn into tadpoles, which undergo metamorphosis.
III. Reptiles.-
Terrestrial cold-blooded or poikilotherm vertebrates which breathe through lungs. The skin of these animals is covered by horny scales to prevent water loss. They are oviparous with internal fertilization and the female lays the eggs on land. These eggs have a soft shell so they don’t dry up.
Reptiles, with the exception of snakes, have four legs. The also have eyelids. Their lungs and circulatory system are more efficient than those of amphibians, having a heart with four chambers (although not completely separate); and their nervous system is also more developed.
Although most reptiles are completely land animals, there are a few which have re-adapted to water such as some snakes and turtles.
Some examples of reptiles are: extinct dinosaurs, lizards, geckos, iguana, snakes, turtles, tortoises, crocodiles, and alligators.
IV. Birds.-
Although most reptiles are completely land animals, there are a few which have re-adapted to water such as some snakes and turtles.
Some examples of reptiles are: extinct dinosaurs, lizards, geckos, iguana, snakes, turtles, tortoises, crocodiles, and alligators.
IV. Birds.-
These are warm-blooded or homoiotherm vertebrates. Birds are terrestrial animals with feathers, wings and a beak. Most of them fly. They breathe through lungs and are oviparous with internal fertilization. Their eggs present a hard shell.
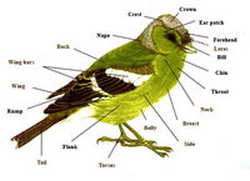
All birds have a neck which joins the head and the trunk. Their forward extremities have evolved into wings. Their heart has two auricles and two ventricles completely separate. Birds have strong but light bones since they have spaces with air.
Their beak is a very special organ used for a wide range of things. Its shape tells you about their nutrition. For example, an eagle’s beak is hooked for tearing meat.
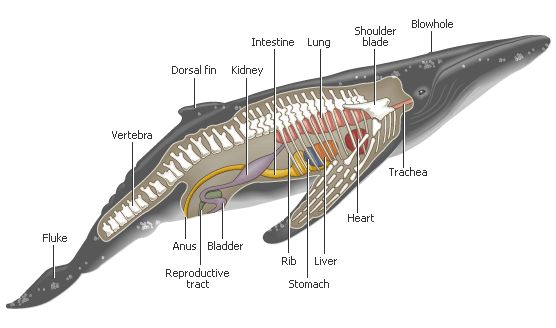
V. Mammals
Their beak is a very special organ used for a wide range of things. Its shape tells you about their nutrition. For example, an eagle’s beak is hooked for tearing meat.
V. Mammals
Most mammals are land vertebrates. They are warm-blooded or homoeothermic creatures. Their body is covered with hair; they have teeth, mammary glands and breathe through lungs. They are viviparous, with internal fertilization.
Mammals are found in all ecosystems. Mammals can be carnivorous, omnivorous or herbivores.
Mammals normally give birth to live young which are nourished in a womb with a placenta. All female mammals have mammary glands to suckle their young until they are old enough to become independent.
Their nervous system as well as their sense organs are quite developed. In most mammals, the backbone is long and continues outside of their body into a tail.
Mammals normally give birth to live young which are nourished in a womb with a placenta. All female mammals have mammary glands to suckle their young until they are old enough to become independent.
Their nervous system as well as their sense organs are quite developed. In most mammals, the backbone is long and continues outside of their body into a tail.
Tasks:
References