Unit 3b - The Hydrosphere and the Biosphere
Key concept - Systems - How do different environmental systems interact with each other on Earth?
Related concepts - Models and environment - How can we use scientific models to explain changes in our environment?
Global concept - Orientations in time and space - Why is the position of Earth in the solar system essential for our survival?
Related concepts - Models and environment - How can we use scientific models to explain changes in our environment?
Global concept - Orientations in time and space - Why is the position of Earth in the solar system essential for our survival?
Unit 4 KEYWORDS
|
|
|
|
The hydrosphereDefinition: The hydrosphere is the system containing all of the water on Earth.
Water is essential for life on Earth as it is required by ALL living organisms. The chemical formula for water is H2O. This means that it contains 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom.
|
(Theawkwardyeti.com, 2015)
|
Complete the mini-test below to see what you can remember about changes of state::
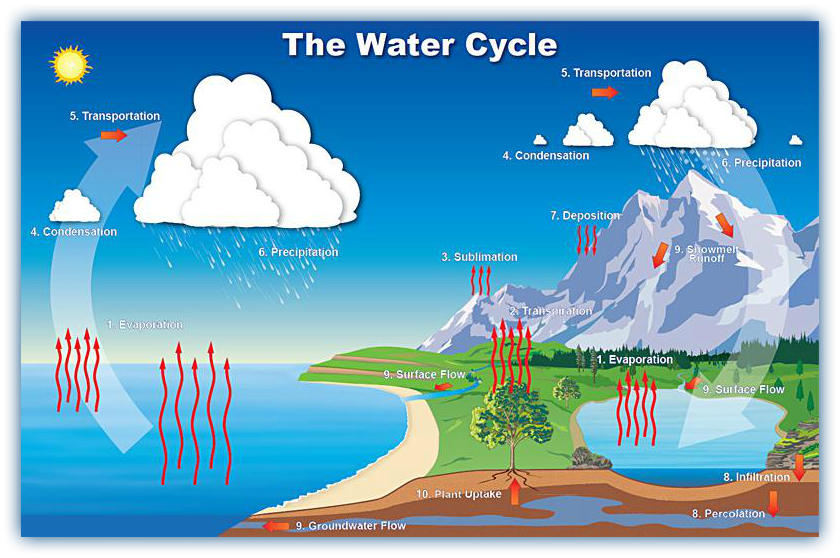
This video explains a simple view of the water cycle and some of the processes in it. You will need to be able to name and describe all of the processes found in the digram below. (Robbins, 2015)
|
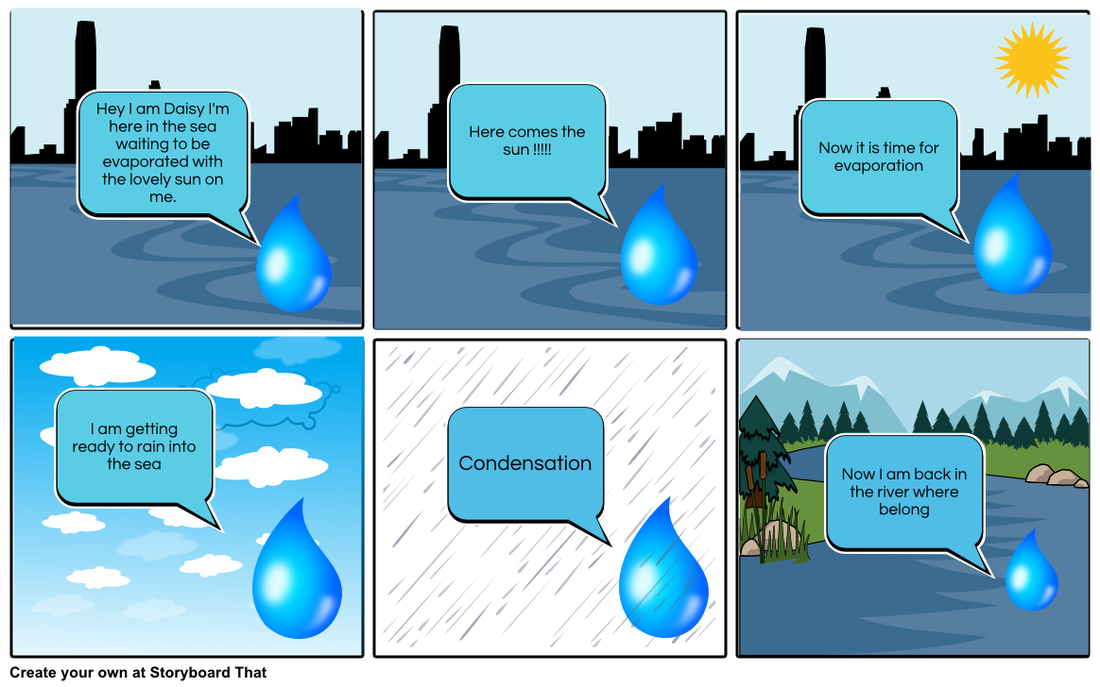
(Storyboardthat.com, 2015)
|
Task 3a: Setup a free account with "storyboardthat.com" and create a cartoon strip called "A Day in the Life of a Water Molecule". Include at least 4 processes and captions to explain what is happening. (Complete it by hand on the document below if you are having problems)
Haz clic aquí para modificar.
| ||||||
The importance of water
|
Although 75% of the Earth is covered in water, only about 3% is freshwater. Freshwater is essential for humans as we need it for agricultural, domestic and industrial purposes.
Nearly 80% of the fresh water on our planet is found as ice in glaciers (Image - (Mail Online, 2010)). Water in this form is not useful for humans so we can only use the water from lakes, rivers and ground water.
Explain why is it difficult and expensive to use seawater? |
|
(Water.org, 2015)
|
Uses:
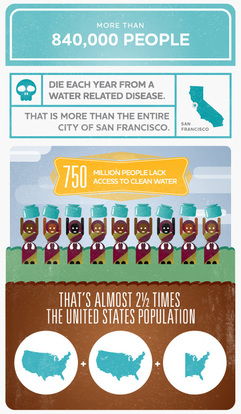
Good quality water is essential for human health. Unfortunately, however, there are still nearly 800 million people around the world who do not have access to clean drinking water.
Which areas of the world have the most people without access to clean drinking water? |
Water pollution
As the amount of fresh water on our planet is limited it is important to keep it clean and usable. Many human activities are now resulting in water pollution.
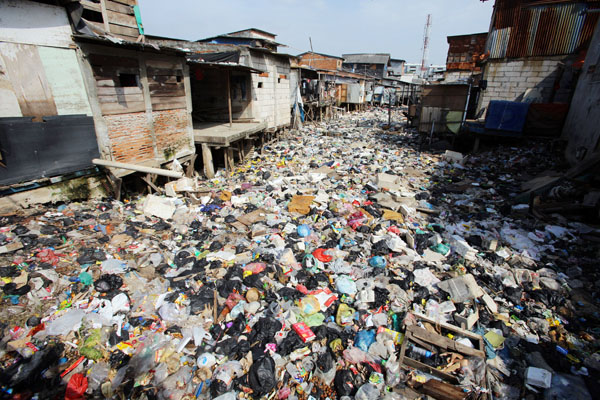
- Domestic water pollution - Water used for washing, cleaning and toilet system contain many harmful chemicals. Waste such as plastic. (Image - Cbunga.wordpress.com, 2015)
- Agricultural water pollution - Chemicals from fertilisers enter groundwater and rivers/lakes. (Image - Greentyne.org.uk, 2015)
- Industrial water pollution - Some of the most harmful chemicals are released by important industrial processes. (Image - Editor, 2015)
Task 3b:
- Match the photos above to the type of water pollution - Domestic, agricultural and industrial.
- Make an informative poster about ways that we can prevent or reduce water pollution.
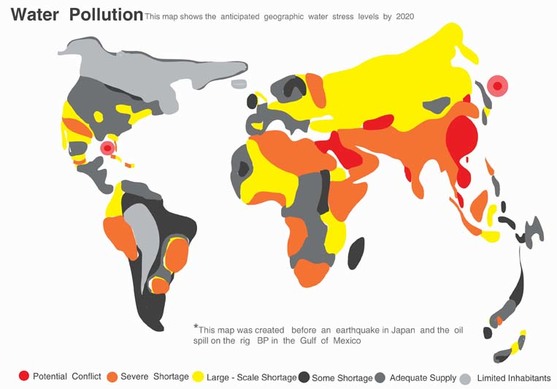
- The following infographic shows the areas of the world that will have the greatest difficulty in obtaining water by the year 2020. State which areas of the world will have the greatest difficulty and explain why you think it is these countries.
(Ecoworldwide.org, 2015)
The Biosphere
Definition: The system of all living things on our planet and the internal systems that are required to maintain it.
In Units 4, 5 and 6 you will learn about life on Earth and the systems in which it functions. The biosphere also includes the systems that we have looked at in Units 2 and 3 - The atmosphere, lithosphere and the hydrosphere. All of these are essential in maintaining life on our planet.
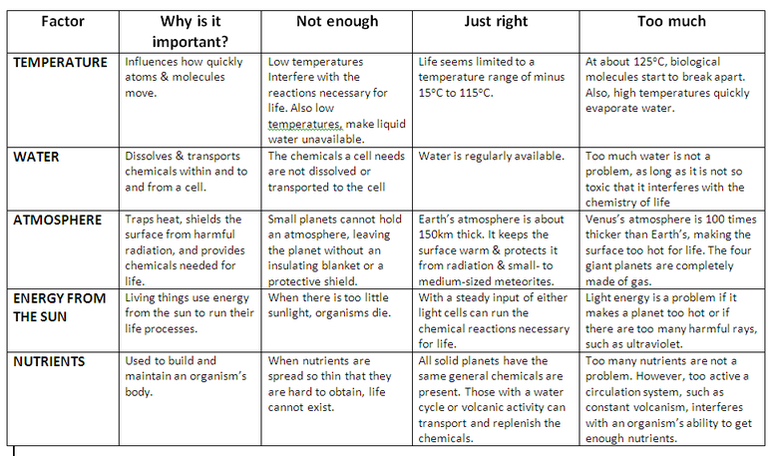
What makes a planet habitable?
The Earth is (for the moment) the only planet we know with a biosphere. When we look at what makes a planet habitable, there are 5 main factors that need to be in balance to create and maintain a biosphere.
References:
ReferencesCbunga.wordpress.com,. (2015). Jakarta | Water pollution - can you see the light at the end of the tunnel?. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from https://cbunga.wordpress.com/tag/jakarta/
Ecoworldwide.org,. (2015). Water Pollution - EcoWorldWide. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://www.ecoworldwide.org/water-pollution/
Editor, N. (2015). – Court Orders EPA to Impose Power Plant Water Pollution Rule | ENS. Ens-newswire.com. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://ens-newswire.com/2013/04/23/court-orders-epa-to-impose-power-plant-water-pollution-rule/
Greentyne.org.uk,. (2015). What Causes River Pollution. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://greentyne.org.uk/what-causes-river-pollution.html
Mail Online,. (2010). 'Climate change could give you cancer': UN report warns of deadly pollutants from glaciers. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-1336810/Climate-change-cancer-UN-report-warns-deadly-pollutants-glaciers.html
Robbins, C. (2015). How regional water-cycle disruptions lead to a drought - iWeatherNet.com.iWeatherNet.com. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://www.iweathernet.com/educational/water-cycle-disruptions-cause-droughts
Storyboardthat.com,. (2015). Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://www.storyboardthat.com/sitemap/storyboards/2014/10/21
Theawkwardyeti.com,. (2015). Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://theawkwardyeti.com/tag/water-cycle/
Water.org,. (2015). Water Facts: Water. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://water.org/water-crisis/water-facts/water/
ReferencesCbunga.wordpress.com,. (2015). Jakarta | Water pollution - can you see the light at the end of the tunnel?. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from https://cbunga.wordpress.com/tag/jakarta/
Ecoworldwide.org,. (2015). Water Pollution - EcoWorldWide. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://www.ecoworldwide.org/water-pollution/
Editor, N. (2015). – Court Orders EPA to Impose Power Plant Water Pollution Rule | ENS. Ens-newswire.com. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://ens-newswire.com/2013/04/23/court-orders-epa-to-impose-power-plant-water-pollution-rule/
Greentyne.org.uk,. (2015). What Causes River Pollution. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://greentyne.org.uk/what-causes-river-pollution.html
Mail Online,. (2010). 'Climate change could give you cancer': UN report warns of deadly pollutants from glaciers. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://www.dailymail.co.uk/sciencetech/article-1336810/Climate-change-cancer-UN-report-warns-deadly-pollutants-glaciers.html
Robbins, C. (2015). How regional water-cycle disruptions lead to a drought - iWeatherNet.com.iWeatherNet.com. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://www.iweathernet.com/educational/water-cycle-disruptions-cause-droughts
Storyboardthat.com,. (2015). Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://www.storyboardthat.com/sitemap/storyboards/2014/10/21
Theawkwardyeti.com,. (2015). Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://theawkwardyeti.com/tag/water-cycle/
Water.org,. (2015). Water Facts: Water. Retrieved 3 July 2015, from http://water.org/water-crisis/water-facts/water/