The endocrine system
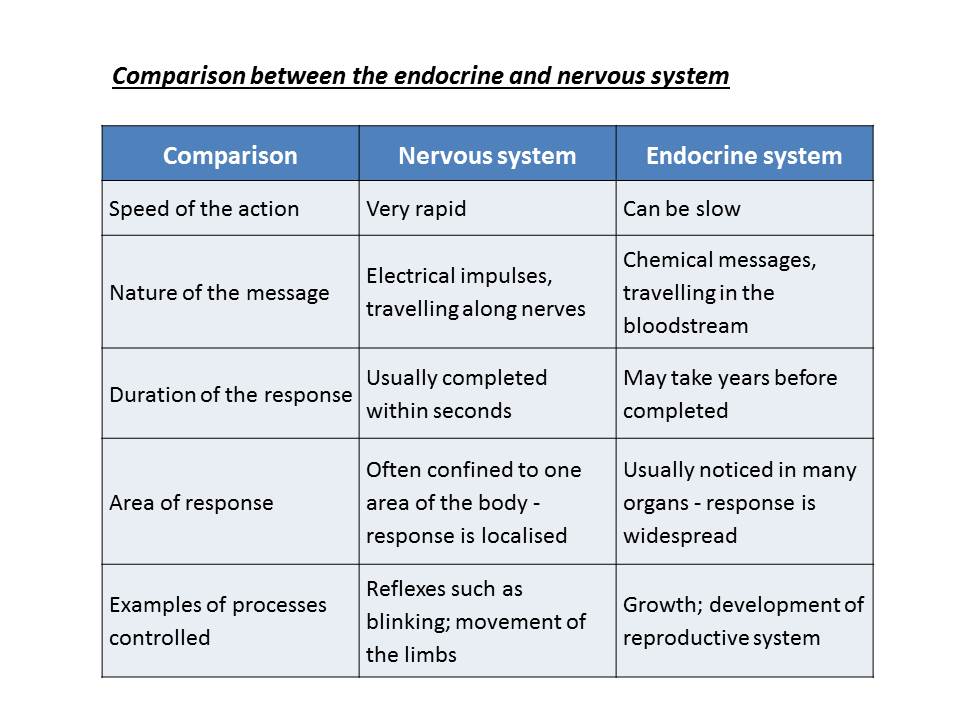
As mentioned at the beginning of the unit, the responses controlled by the nervous system happen quickly. However, some there are some responses that go over a long period of time, such as growth and development. These sort of functions are controlled by the endocrine system.
The endocrine system coordinates and performs its functions by the use of organs called endocrine glands. These glands secrete chemicals called hormones. The prefix ‘endo’ means interior, the endocrine system works exclusively on the interior of the body. The endocrine glands are ductless, so hormones are directly released in the bloodstream. The hormones, once released travel in the blood to any part of the body that is supplied with blood, reaching all tissues but affecting only the target organs.
Hormones are chemical messengers which are transported in the bloodstream. They work slowly, over time and affect different processes such as: growth and development, metabolism (how your body gets energy from the foods you eat), sexual function, reproduction and mood.
The endocrine system coordinates and performs its functions by the use of organs called endocrine glands. These glands secrete chemicals called hormones. The prefix ‘endo’ means interior, the endocrine system works exclusively on the interior of the body. The endocrine glands are ductless, so hormones are directly released in the bloodstream. The hormones, once released travel in the blood to any part of the body that is supplied with blood, reaching all tissues but affecting only the target organs.
Hormones are chemical messengers which are transported in the bloodstream. They work slowly, over time and affect different processes such as: growth and development, metabolism (how your body gets energy from the foods you eat), sexual function, reproduction and mood.
What do hormones do?
Hormones control growth, development, metabolism, sugar levels and other processes in the body. One of the most significant processes controlled by hormones are the changes taking place in puberty. At puberty a person becomes physically able to reproduce. The brain instructs the pituitary gland (located on the downside of the brain) to stimulate primary sex organs to develop (testes in man and ovaries in women).The sex-hormones oestrogen (in females) and testosterone (in males) are released into the bloodstream and circulate through the body. They are only effective on the target organs.
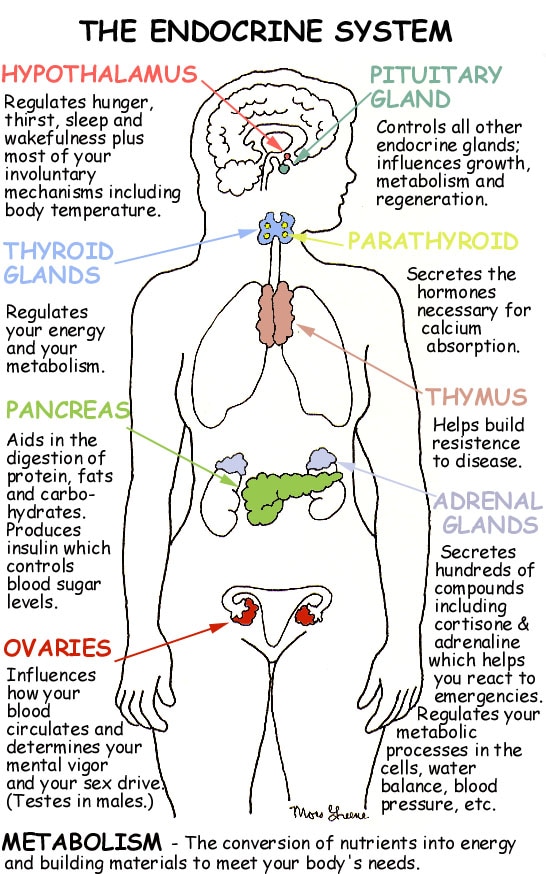
Examples of glands and their hormones (Remember a few examples from this diagram)
Hormones control growth, development, metabolism, sugar levels and other processes in the body. One of the most significant processes controlled by hormones are the changes taking place in puberty. At puberty a person becomes physically able to reproduce. The brain instructs the pituitary gland (located on the downside of the brain) to stimulate primary sex organs to develop (testes in man and ovaries in women).The sex-hormones oestrogen (in females) and testosterone (in males) are released into the bloodstream and circulate through the body. They are only effective on the target organs.
Examples of glands and their hormones (Remember a few examples from this diagram)
Examples of glands and their hormones
The pituitary gland
This is the most important hormonal gland as it controls the rest of the endocrine system. It is on its turn controlled the hypothalamus which is part of the nervous system. Make sure you understand the relation between the two and the fact that the endocrine system is controlled by the nervous system. One of the hormones it produces is the Human growth hormone, for growth and development.
The Thyroid gland
The thyroid gland produces Thyroxine, a hormone which controls the rate of metabolism and body mass.
The Adrenal gland
This gland produces adrenaline. Adrenaline prepares your body for fight or flight in potentially dangerous situations. It alters your heart rate, your respiration rate, dilates your pupils, liberates glucose for extra energy and makes you very concentrated on the danger so you have more probability to survive
The pituitary gland
This is the most important hormonal gland as it controls the rest of the endocrine system. It is on its turn controlled the hypothalamus which is part of the nervous system. Make sure you understand the relation between the two and the fact that the endocrine system is controlled by the nervous system. One of the hormones it produces is the Human growth hormone, for growth and development.
The Thyroid gland
The thyroid gland produces Thyroxine, a hormone which controls the rate of metabolism and body mass.
The Adrenal gland
This gland produces adrenaline. Adrenaline prepares your body for fight or flight in potentially dangerous situations. It alters your heart rate, your respiration rate, dilates your pupils, liberates glucose for extra energy and makes you very concentrated on the danger so you have more probability to survive
Hormones and puberty
Recommended watching
The thyroid
References
Cabrera Calero, A. & Sanz Esteban, M. (2011). Biología y geología, 3º ESO, Andalucía. San Fernando de Henares, Madrid: Oxford Educación.
Campbell, N. (1993). Biology. Redwood City, Calif.: Benjamin/Cummings. Headwayguernsey.com, (2016). Headway Guernsey. [online] Available at: http://www.headwayguernsey.com/ [Accessed 14 Feb. 2016].
Pickering, W. (2006). Complete biology for IGCSE. Oxford [England]: Oxford University Press.
Qld Science Teachers, (2016). Qld Science Teachers. [online] Available at: http://www.qldscienceteachers.com/ [Accessed 14 Feb. 2016].
Cabrera Calero, A. & Sanz Esteban, M. (2011). Biología y geología, 3º ESO, Andalucía. San Fernando de Henares, Madrid: Oxford Educación.
Campbell, N. (1993). Biology. Redwood City, Calif.: Benjamin/Cummings. Headwayguernsey.com, (2016). Headway Guernsey. [online] Available at: http://www.headwayguernsey.com/ [Accessed 14 Feb. 2016].
Pickering, W. (2006). Complete biology for IGCSE. Oxford [England]: Oxford University Press.
Qld Science Teachers, (2016). Qld Science Teachers. [online] Available at: http://www.qldscienceteachers.com/ [Accessed 14 Feb. 2016].