Unit 6b - THE CHANGING SURFACE OF THE EARTH
Key concept - Relationships- How do differen
Related concepts - Interaction and Balance - Try to imagine
Global concept - Scientific and technical innovation - Do you think Science and Techno
Related concepts - Interaction and Balance - Try to imagine
Global concept - Scientific and technical innovation - Do you think Science and Techno
Unit 6B Keywords
|
|
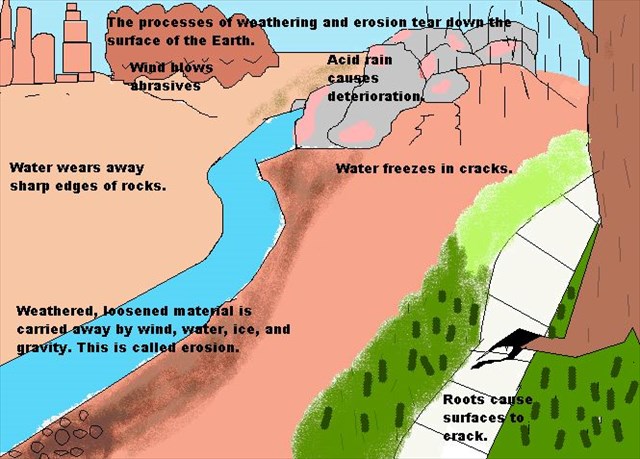
The landscape is a consequence of the action of two types of geological processes; internal and external geological processes.
- Internal geological processes are driven by the internal energy of our Earth. They build the land relief (e.g. they are the ones responsible for the appearance of mountain ranges etc). The internal geological processes are earthquakes and volcanic activity.
- External geological processes are driven by the external energy that comes from the Sun and gravity. The changes the land relief undergoes is because of these processes, which are weathering, erosion, transport and deposition.
Geological Agents
There are a series of natural systems that carry out the different geological processes, known as the geological agents. These geological agents carry out the modelling of the land relief. The external geological agents are the wind, the water, living beings and gravity.
The wind and the water are dynamic agents, which are driven by the energy that comes from the Sun. Living beings; animals, plants and microorganisms, are also dynamic agents that change the earth’s surface. Gravity is a static agent which is always present in all the processes carried on by the dynamic agents.
- The wind acts mainly in areas where there is no vegetation, such as the beach or a desert. The wind can easily pick up the smallest, fine grains of material and transport them somewhere else. On the other hand, water is the most important external geological agent, acting in all of its forms, rain, glaciers, rives, the sea etc.
- Glaciers have a great erosive and transportation capacity. Glaciers can only be found in permanent frost areas.
- Rivers are natural, usually permanent watercourses flowing toward an ocean, a sea, a lake or another river. Their erosive and transportation capacity will be determined by the speed of their flow as well as their steepness, which at the same time will depend upon the climate of the area, and location of the river (high mountain or a valley).
- Groundwater flows principally downward under the influence of gravity, through soils, sediments, and rocks. They will dissolve soluble underground rocks, in particular limestone and gypsum. As a result we will have the formation of caves, stalactites, etc.
- The sea will act mainly along the shoreline, and we can see the result of this erosive agent on the cliffs.
The changes on the earth’s surface is the best evidence of the action of these agents which act with a greater or lower intensity depending on the climate and the chemical composition of rocks.
External Geological Processes
The external geological processes driven by the energy provided by the Sun and gravity are: weathering, erosion, transport and deposition (sedimentation).
Weathering
Rain, frost, and the heating effect of the Sun weaken and loosen the surface of the rock.
We will consider three types of weathering: mechanical, chemical and biological.
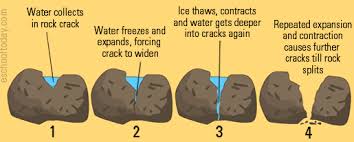
- Mechanical weathering: When the main agent responsible for the breaking of a rock is the temperature. Mechanical or physical weathering is the breaking down of rock into smaller pieces without any chemical changes in the rock itself.
This type of action can occur in a number of ways, one example being frost or ice wedging – water seeps into cracks and pores in a rock and freezes, expands, exerts pressure within the crack or pore and causes pieces of the rock to break off.
- Chemical weathering: In chemical weathering, chemical changes take place in the rock, forming new products that can be carried away more easily than the original rock. Areas where water is present or the air is humid are subject to chemical weathering. The main agents responsible for the alteration of rocks are the CO2, water vapour and oxygen, found in the atmosphere.
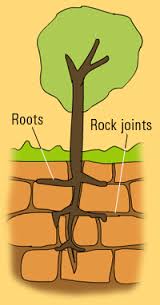
- Biological weathering: It is a mixture of mechanical and chemical weathering carried out by living beings. Some plants can easily break rocks. The roots grow through existing cracks in the rocks. The growth causes the root to expand, forcing the crack to expand, forcing the crack to widen. This force can eventually split the rock apart. Also, many plants, algae and fungi produce chemical substances that may alter some minerals. Animals that live in the soil (moles, insects, worms etc) cause a lot of weathering. By burrowing in the ground, these animals brake up soil and loosen rocks to be exposed to further weathering.
Erosion, transport and deposition
fragmented rocks.
3.Deposition (or sedimentation) of the transported materials. It usually takes place in the lower parts of the crust, forming layers of sediments.
- Erosion or fragmentation of rocks, can be carried out by water, the wind, ice, and the particles transported by these agents. Erosion is a dynamic process with transportation of the materials.2.
- Transport of the materials torn off by erosion which is usually carried out by water or wind.
fragmented rocks.
3.Deposition (or sedimentation) of the transported materials. It usually takes place in the lower parts of the crust, forming layers of sediments.
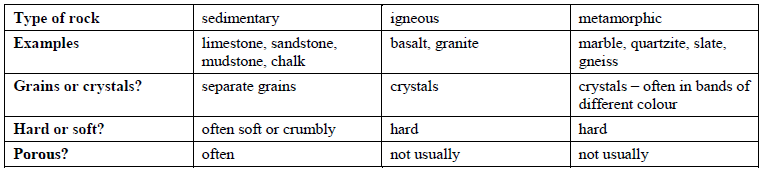
Types of rocks
Sedimentary rocks
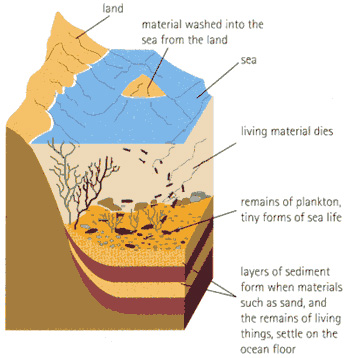
Rock fragments, formed as a result of weathering and erosion, are transported by rivers, and the fragments get worn down. Small rock fragments are called grains. When the water slows down, some of the grains are deposited at the bottom of rivers, lakes or seas, and form sediment.
Layers of sediment collect on the sea bed, and the bottom layers get squashed. The grains of sediment are forced closer together (compacted) and the water is squeezed out from between the grains. Minerals in the sediment ‘glue’ the grains of rock together (cementation). Eventually, sedimentary rock is formed. The composition of sedimentary rocks varies and depends on the way they were formed. For example, there are different types of limestone – chalk is formed from the shells of microscopic animals, coquina is formed from larger shell fragments and oolite is formed from sediments deposited when sea water evaporated.
If any animals or plants get trapped in the sediment, they may form fossils.
Igneous rocks
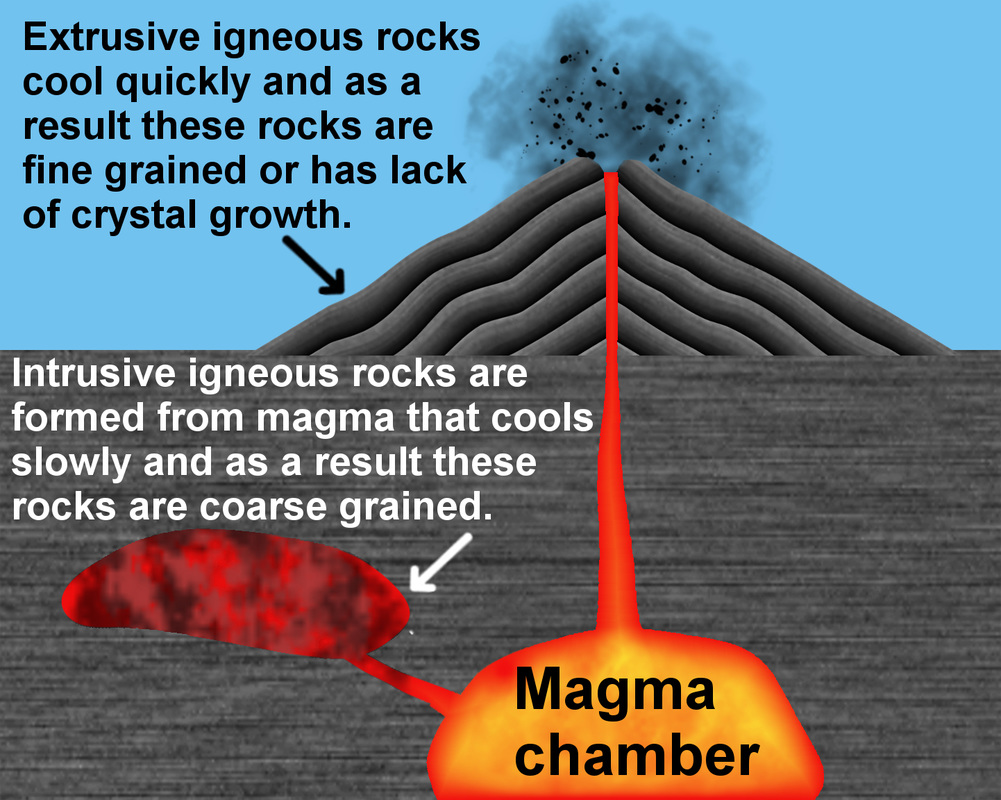
Molten rock is called magma. If the molten rock flows out of volcanoes it is called lava. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools down.
Lava cools down quite quickly, and forms igneous rocks with small crystals (like basalt). Magma underground cools down much more slowly and forms rocks, like granite, with bigger crystals.
Molten rock is called magma. If the molten rock flows out of volcanoes it is called lava. Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools down.
Lava cools down quite quickly, and forms igneous rocks with small crystals (like basalt). Magma underground cools down much more slowly and forms rocks, like granite, with bigger crystals.
Metamorphic rocks
Sedimentary or igneous rocks can be changed by heat or pressure into new kinds of rock, called metamorphic rocks. Metamorphic rocks have different properties from the sedimentary or igneous rocks they were made from.
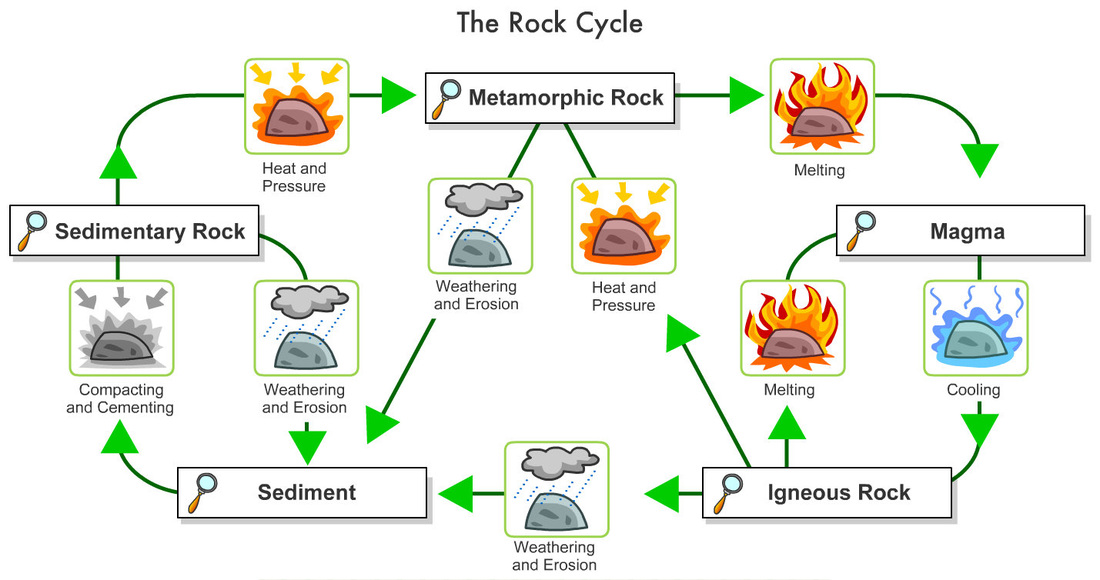
The rock cycle
Click here for an animated rock cycle
The Earth is continually changing. Rocks are weathered and eroded and new rocks are being
formed. The processes which make rocks, weather them and change them are linked together in
the rock cycle
Seismic activity is caused by the movement of the Earth´s tectonic plates.
Tasks:
1. Where does the energy to move these plates come from?
2. What effects can be seen on the Earth´s surface?
Tasks:
1. Where does the energy to move these plates come from?
2. What effects can be seen on the Earth´s surface?