Infertility, contraception and STDs
|
|
|
Infertility refers to the inability to have children using natural methods. It can occur in both men and women, and there are many different causes:
|
Male infertility
Low sperm count Defective sperm Sperm incompatible with cervical mucus |
Female infertility
No ovulation or problems with ovulation Fallopian tube obstruction Uterine abnormalities which make it difficult for the embryo to implant |
Nowadays, there are many assisted reproduction techniques used to help people who have infertility problems to have children.
Contraceptive methods can be used to avoid getting pregnant during sexual intercourse. There are natural and artificial methods of contraception.
Natural methods take into account the cyclical character of female fertility, and require that the couple adapt their sexual activity to the woman’s menstrual cycle. These methods are a lot less reliable than other types of contraception.
Artificial methods are used to prevent fertilisation at any time. They do not involve adapting sexual activity to the menstrual cycle.
Contraceptive methods can be used to avoid getting pregnant during sexual intercourse. There are natural and artificial methods of contraception.
Natural methods take into account the cyclical character of female fertility, and require that the couple adapt their sexual activity to the woman’s menstrual cycle. These methods are a lot less reliable than other types of contraception.
Artificial methods are used to prevent fertilisation at any time. They do not involve adapting sexual activity to the menstrual cycle.
Natural methods of contraception
Artificial methods of contraception
A diaphragm or cup is a thin rubber with a springy outer ring to ensure a close fit. It prevents sperm from entering the uterus. It is often used with a spermicide cream.
IUD (intrauterine device) can be with or without hormones. It is a plastic-coated copper coil which may be left in the uterus for months or even for years.
The morning-after pill is taken 48-72 hours after intercourse. It is not for regular use, but a doctor may prescribe it if there is a risk of unwanted pregnancy which might lead to an abortion at a later date. This pill contains hormones which cause the lining of the uterus to be shed. The 5-day morning-after pill is similar to the morning-after but need to be taken 120h after sexual intercourse.
Fitting an IUD within 72-96 hours of intercourse usually prevents pregnancy as well.
In a vasectomy the two sperm ducts are cut and tied in a surgical operation. Vasectomy, though complicated, can be reversed by an operation.
Remember that of all the above methods, only the condom will protect you against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), by reducing the risk of catching them.
- Rhythm method: couples who use this method avoid having sexual intercourse during the fertile days of the woman’s period.
- Basal body temperature: the woman measures her body temperature and looks for changes at ovulation.
- Billings: the woman notes changes that take place in the mucus of the vagina and cervix at ovulation.
- Sympto- thermal: a combination of the above three methods.
- Withdrawal or Coitus interruptus: the penis is withdrawn from the vagina before ejaculation. Of the natural methods this is probably the most unreliable, as small amounts of semen can leak out before the ejaculation.
Artificial methods of contraception
- Barrier methods: these methods physically prevent sperm from reaching the egg. They include male condoms, female condoms, diaphragms and IUD (intrauterine devices)
A diaphragm or cup is a thin rubber with a springy outer ring to ensure a close fit. It prevents sperm from entering the uterus. It is often used with a spermicide cream.
IUD (intrauterine device) can be with or without hormones. It is a plastic-coated copper coil which may be left in the uterus for months or even for years.
- Chemical methods: These are chemical barriers and include spermicide creams, hormonal contraceptive (such as the pill), the morning-after pill and the 5-day morning-after pill.
The morning-after pill is taken 48-72 hours after intercourse. It is not for regular use, but a doctor may prescribe it if there is a risk of unwanted pregnancy which might lead to an abortion at a later date. This pill contains hormones which cause the lining of the uterus to be shed. The 5-day morning-after pill is similar to the morning-after but need to be taken 120h after sexual intercourse.
Fitting an IUD within 72-96 hours of intercourse usually prevents pregnancy as well.
- Surgical methods: there are two surgeries that are used to permanently prevent fertilisation: tubal ligation for women, and vasectomy for men.
In a vasectomy the two sperm ducts are cut and tied in a surgical operation. Vasectomy, though complicated, can be reversed by an operation.
Remember that of all the above methods, only the condom will protect you against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), by reducing the risk of catching them.
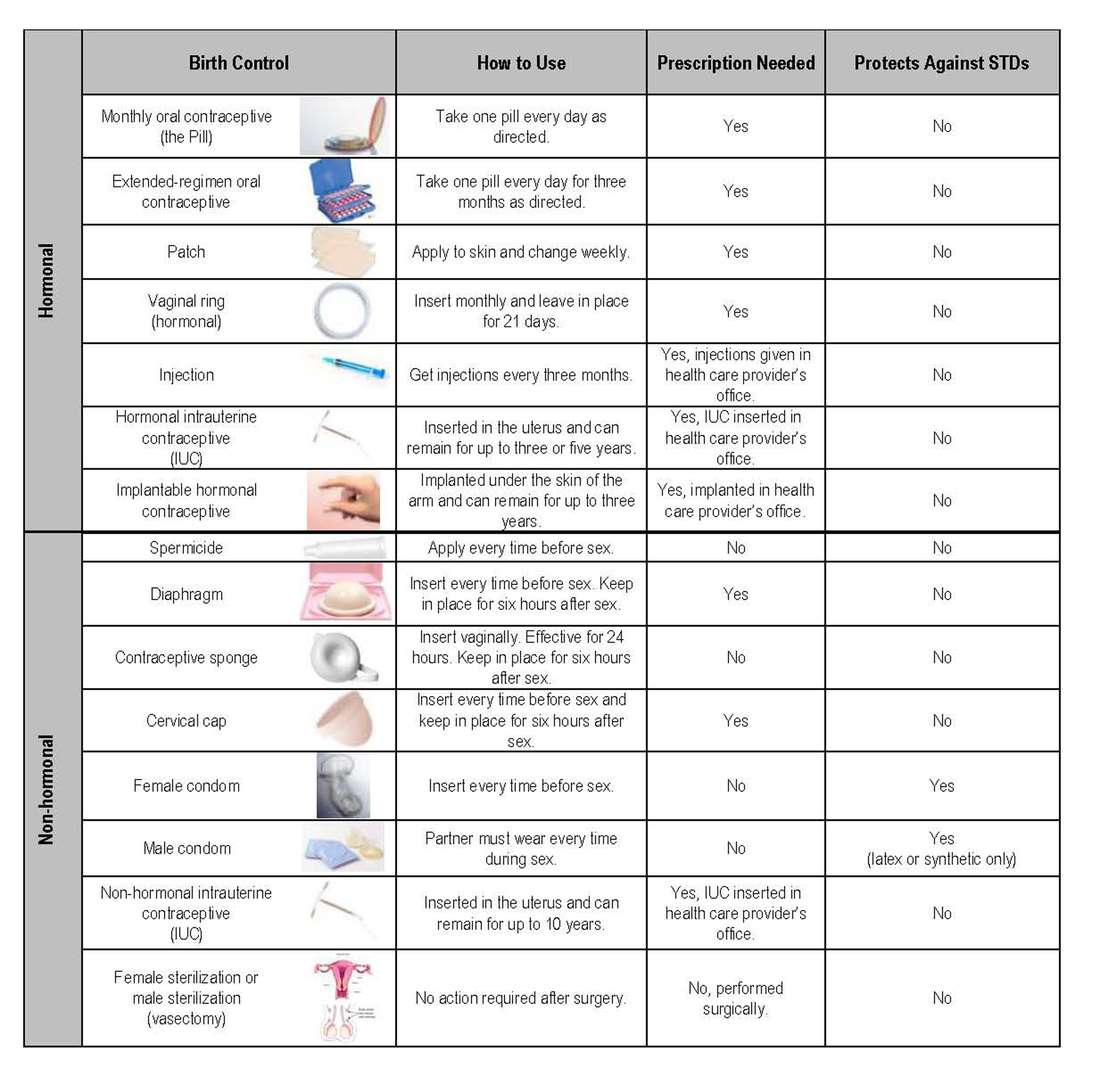
Birth control methods
Table from:
Virginiawomenscenter.com, (2014). [online] Available at: http://www.virginiawomenscenter.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/Selecting-the-Right-Birth-Control-Method-For-You.jpg [Accessed 10 Jun. 2014].
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that you can get from having sex with someone who has the infection. The causes of STDs are bacteria, parasites and viruses. There are more than 20 types of STDs, including
Most STDs affect both men and women, but in many cases the health problems they cause can be more severe for women. If a pregnant woman has an STD, it can cause serious health problems for the baby.
If you have an STD caused by bacteria or parasites, your health care provider can treat it with antibiotics or other medicines. If you have an STD caused by a virus, there is no cure. Sometimes medicines can keep the disease under control. However, some STDs can lead to death.
Correct usage of latex condoms greatly reduces, but does not completely eliminate, the risk of catching or spreading STDs.
Most STDs affect both men and women, but in many cases the health problems they cause can be more severe for women. If a pregnant woman has an STD, it can cause serious health problems for the baby.
If you have an STD caused by bacteria or parasites, your health care provider can treat it with antibiotics or other medicines. If you have an STD caused by a virus, there is no cure. Sometimes medicines can keep the disease under control. However, some STDs can lead to death.
Correct usage of latex condoms greatly reduces, but does not completely eliminate, the risk of catching or spreading STDs.