Kingdom Fungi
Key words
- kingdom, (-s)
- phylum, phyla
- class, (-es)
- fungus, fungi
- alga, algae
- symbiosis, symbioses
- parasite, (-s) / host,(-es)
This kingdom is made up by eukaryotic organisms, the vast majority multicellular, but also unicellular, and they do not have tissues. They are all heterotrophic.
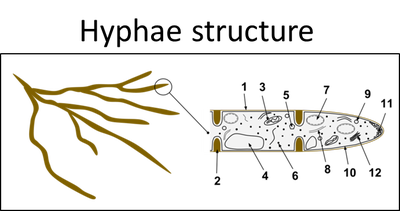
The body structure of the fungi is unique. The cells in fungi are grouped together to make up filaments called hyphae. The web of hyphae is called a mycelium. Fungi reproduce by spores, which are specialised reproductive cells.
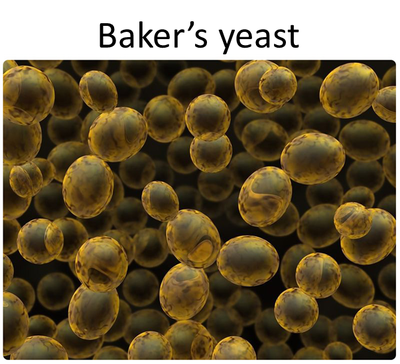
Fungi are a very varied kingdom and they can be classified into three groups: the microscopic fungi (yeasts), the moulds and the mushrooms and toadstools. Fungi usually live in damp places. Some fungi are parasites causing diseases to their host. But others live together, in a symbiotic relationship, like the lichens. Most fungi are decomposers.
The body structure of the fungi is unique. The cells in fungi are grouped together to make up filaments called hyphae. The web of hyphae is called a mycelium. Fungi reproduce by spores, which are specialised reproductive cells.
Fungi are a very varied kingdom and they can be classified into three groups: the microscopic fungi (yeasts), the moulds and the mushrooms and toadstools. Fungi usually live in damp places. Some fungi are parasites causing diseases to their host. But others live together, in a symbiotic relationship, like the lichens. Most fungi are decomposers.
NOTE: A lichen is a symbiotic relationship between a fungi and an algae. A symbiosis is an association between two organisms of different species that benefit each member.
Points to remember:
•Eukaryotes
•Single (yeasts) and multicellular (filamentous - macroscopic)
•Have a mycelium that consists of hyphae.
•Cell walls made of chitin
•Mostly free-living
•Extra-cellular digestion - excreting enzymes and absorbing soluble products.
•Reproduction by release of spores.
•Single (yeasts) and multicellular (filamentous - macroscopic)
•Have a mycelium that consists of hyphae.
•Cell walls made of chitin
•Mostly free-living
•Extra-cellular digestion - excreting enzymes and absorbing soluble products.
•Reproduction by release of spores.