The periodic table of elements
History of Mendeleev and the Periodic Table
Dmitri Mendeleev was a Russian chemist and inventor. He is credited as being the creator of the first version of the periodic table of elements. Using the table, he predicted the properties of elements yet to be discovered.
Other scientists had suggested in the 1860s that the elements display trends in their properties that could be used to put them into a table of periodicity. John Newlands published his Law of Octaves in 1865. The lack of spaces for undiscovered elements and the placing of two elements in one box was criticized and his ideas were not accepted. Another was Lothar Meyer, who published a paper in 1864 describing 28 elements. Neither attempted to predict new elements. In 1863 there were 56 known elements with a new element being discovered at a rate of approximately one per year (BBC.co.uk, 2015).
After becoming a teacher, Mendeleev wrote the definitive textbook of his time: Principles of Chemistry. As he attempted to classify the elements according to their chemical properties, he noticed patterns that led him to postulate his periodic table. Mendeleev was unaware of the other work on periodic tables going on in the 1860s. He made a table, and by adding additional elements following this pattern, developed his extended version of the periodic table..
Dmitri Mendeleev was a Russian chemist and inventor. He is credited as being the creator of the first version of the periodic table of elements. Using the table, he predicted the properties of elements yet to be discovered.
Other scientists had suggested in the 1860s that the elements display trends in their properties that could be used to put them into a table of periodicity. John Newlands published his Law of Octaves in 1865. The lack of spaces for undiscovered elements and the placing of two elements in one box was criticized and his ideas were not accepted. Another was Lothar Meyer, who published a paper in 1864 describing 28 elements. Neither attempted to predict new elements. In 1863 there were 56 known elements with a new element being discovered at a rate of approximately one per year (BBC.co.uk, 2015).
After becoming a teacher, Mendeleev wrote the definitive textbook of his time: Principles of Chemistry. As he attempted to classify the elements according to their chemical properties, he noticed patterns that led him to postulate his periodic table. Mendeleev was unaware of the other work on periodic tables going on in the 1860s. He made a table, and by adding additional elements following this pattern, developed his extended version of the periodic table..
|
|
|
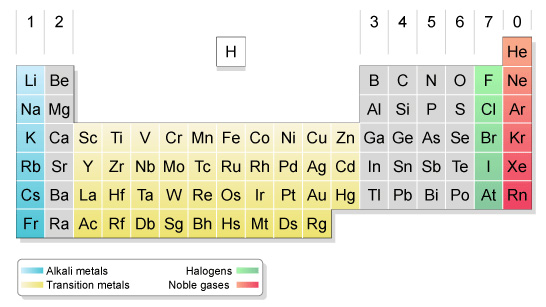
This method of arranging the elements shows that the patterns in their properties are linked to their atomic number. If all atoms have the same number of protons as electrons, then this means that the elements are also arranged according to the number of electrons they have.
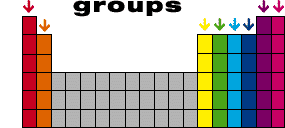
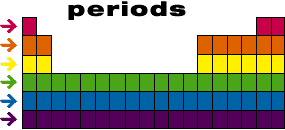
How are the elements organised on the periodic table?
The elements are arranged in columns, known as groups, and rows, called periods. When you know what group and period an atom is in, you know lots of detail about its structure so you can predict how it will react with other elements.
Important points to remember:
- The elements are ordered by their atomic number.
- In each group, 1 electron is added to the outer shell of the atom.
- In each period a new electron shell is added. to the atom.
- The Periodic Table lists only elements and not compounds or mixtures!
- Most of the elements are metals.
- Only about 20 of the elements are non-metals.
(Edcoogle Blog, 2015)
Try to learn the names of the different groups!
(BBC.co.uk, 2015)
How do different groups react?
|
|
|
Understanding the structure of elements allows us to understand how they might react together and what compounds may be formed. We can use this knowledge to make chemical processes more efficient and make more money in real-life. It also helps us name the compounds with an internationally-agreed upon system. This is called chemical formulation.
Click on the button below to go the chemical formulation section of this website
Task 4e:
Answer the following questions in your NSD:
Answer the following questions in your NSD:
- Which elements had complete outer shells? Give the name and symbol for each.
- What do you notice about the elements in Group 1? What is the common name for Group 1?
- What do you notice about the number of electrons in the outer shell as you move left-to-right across the table?
- What do you notice about the number as shells as you move down the table?
- Predict the number of valence electrons for each of the following elements, based on their position in the table: Barium, Lead, Xenon Potassium,
- Extension: How would you classify hydrogen? Why
References
Bbc.co.uk,. (2015). BBC - GCSE Bitesize: Mendeleev's periodic table. Retrieved 7 July 2015, from http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/edexcel_pre_2011/patterns/periodictablerev4.shtml
Edcoogle Blog,. (2015). What is periodic table and how to read the periodic table?. Retrieved 7 July 2015, from http://www.edcoogle.com/blog/2015/04/what-is-periodic-table-how-to-read-the-periodic-table-elements/
Studios, A. (2015). Chem4Kids.com: Elements & Periodic Table: Periodic Table. Chem4kids.com. Retrieved 7 July 2015, from http://www.chem4kids.com/files/elem_pertable.html
Bbc.co.uk,. (2015). BBC - GCSE Bitesize: Mendeleev's periodic table. Retrieved 7 July 2015, from http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/edexcel_pre_2011/patterns/periodictablerev4.shtml
Edcoogle Blog,. (2015). What is periodic table and how to read the periodic table?. Retrieved 7 July 2015, from http://www.edcoogle.com/blog/2015/04/what-is-periodic-table-how-to-read-the-periodic-table-elements/
Studios, A. (2015). Chem4Kids.com: Elements & Periodic Table: Periodic Table. Chem4kids.com. Retrieved 7 July 2015, from http://www.chem4kids.com/files/elem_pertable.html